回顾一下,上期介绍了OpenCv的SVM模型训练,这期继续介绍一下识别过程。 这幅流程图还是很经典,直观的。 我们先一下上期说的: OpenCv的中文显示方法 1: 字体simhei.ttf需要下载,然后在font = ImageFont.truetype(“./simhei.ttf”, 20, encoding=“utf-8”)指定simhei.ttf的路径即可 ,同样的需要把这个字体放在的路径找到或者放在运行代码同级,都行。 2: 中文编码为utf-8。否则中文会显示为矩形。str1 = str1.decode(‘utf-8’) 3:上代码: 值得注意的是: 2)opencv读取完图像存储格式是numpy。PIL是自己定义的格式。要调用PIL的方法需要先将numpy转为自己的格式。pilimg = Image.fromarray(cv2img)。相反,PIL处理完后,调用opencv方法要将格式转回numpy。 cv2charimg = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(pilimg), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)。 不转的话会报错。TypeError: Expected cv::UMat for argument ‘src’ 还有一种常用的:freetype方式: 同样的先下载字体:比如上面的simhei.ttf,同样的还有msyh.ttf(这些百度就行,很多): 个人推荐第一种! 接下来继续车牌检测~ 查找图像边缘整体形成的矩形区域,可能有很多,车牌就在其中一个矩形区域中(这也是程序or算法的不足之处不过,并不影响结果) 需要注意的是cv2.findContours()函数接受的参数为二值图,即黑白的(不是灰度图),所以读取的图像要先转成灰度的,再转成二值图! 结果筛选(原因是上述的多可能性情况): 接下来: 矩形区域可能是倾斜的矩形,需要矫正,以便使用颜色定位 开始使用颜色定位,排除不是车牌的矩形,目前只识别蓝、绿、黄车牌 上个表情防止兄弟看得睡着了 部分代码有注释,大致说说: 这是识别车牌中的字符 这个是掩膜方法,我们后续再统一介绍吧, 大致思路就是把原图中要放logo的区域抠出来,再把logo放进去就行了。 根据设定的阈值和图片直方图,找出波峰,用于分隔字符 根据找出的波峰,分隔图片,从而得到逐个字符图片 其中: 是 矩 计算 下期介绍 最后,结果筛选: 返回识别到的字符、定位的车牌图像、车牌颜色 main函数: 最后在此说明:代码非本人原创,来自朋友毕设,过段时间会开源请关注一下博主,谢谢 小结一下: 上图,介绍下期内容:初识CVLIB 最后别忘了给博主一个赞和关注~,码字不易,一起进步! 最后欢迎大家进入我的微信群学习交流,机器&深度学习技术交流群,广结豪杰!大家一起进步,附上微信。 上海第二工业大学智能科学与技术大二 周小夏(CV调包侠)
这期继续SVM实践项目:车牌检测与识别,同时也介绍一些干货
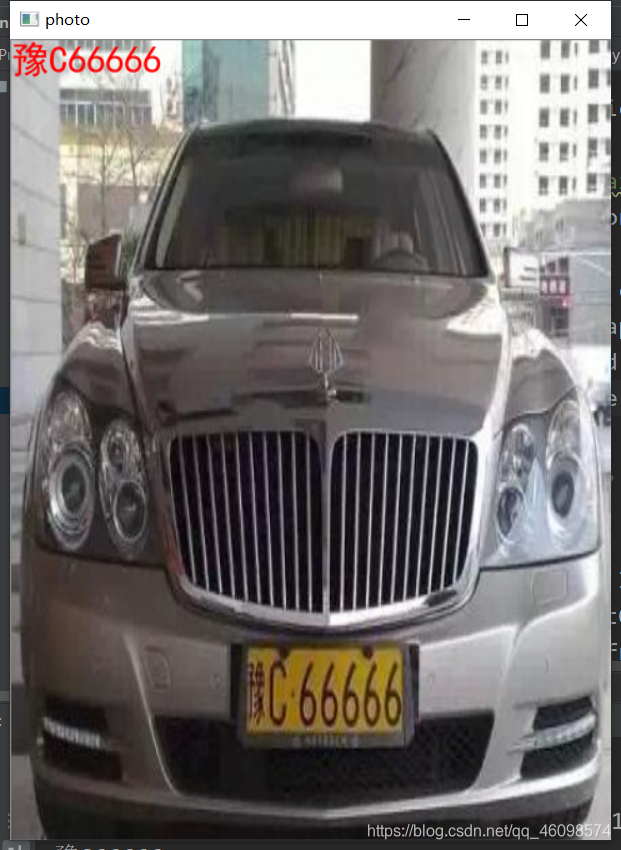
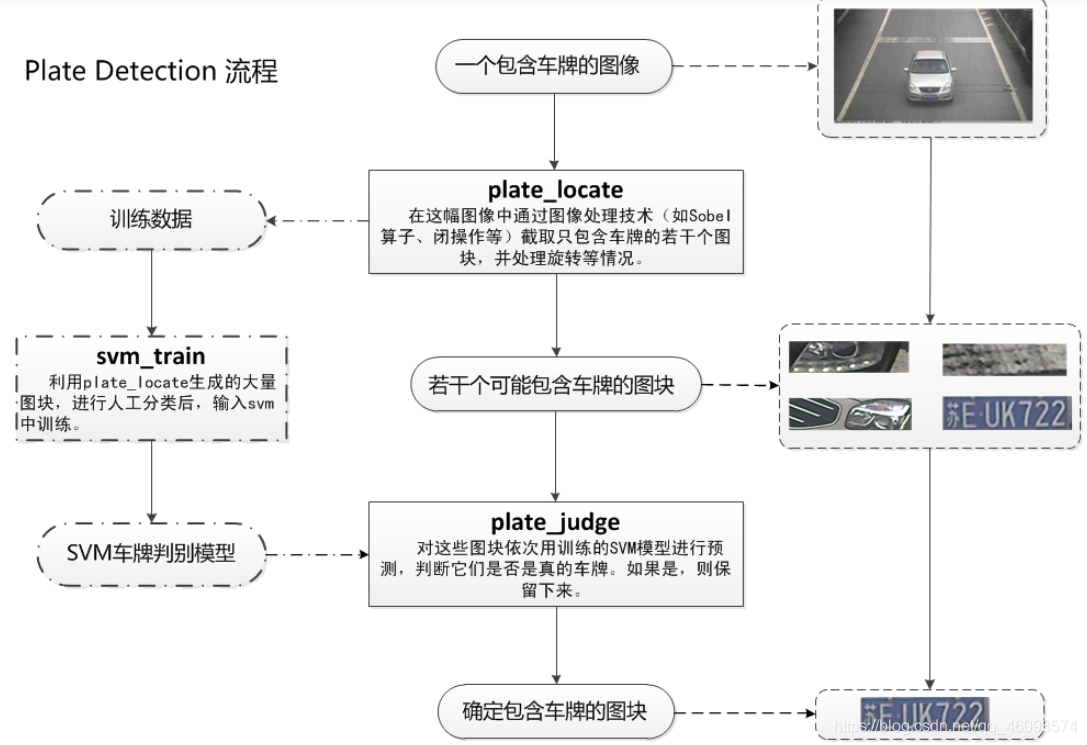

我使用的是PIL的显示方法,下面简介一下教程:
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont import cv2 import numpy as np # cv2读取图片 img = cv2.imread(r'C:UsersacerDesktopblack.jpg') # 名称不能有汉字 cv2img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # cv2和PIL中颜色的hex码的储存顺序不同 pilimg = Image.fromarray(cv2img) # PIL图片上打印汉字 draw = ImageDraw.Draw(pilimg) # 图片上打印 font = ImageFont.truetype("simhei.ttf", 20, encoding="utf-8") # 参数1:字体文件路径,参数2:字体大小 draw.text((0, 0), "Hi", 1.8, (255, 0, 0), font=font) # 参数1:打印坐标,参数2:文本,参数3:字体颜色,参数4:字体 # PIL图片转cv2 图片 cv2charimg = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(pilimg), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) # cv2.imshow("图片", cv2charimg) # 汉字窗口标题显示乱码 cv2.imshow("photo", cv2charimg) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
1)opencv读取图像后图像颜色通道是BGR排列的,而PIL读取的图像是RGB排列的。要注意图像颜色通道排列的转化cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)。#-*- coding: utf-8 -*- import cv2 import ft2 img = cv2.imread('pic_url.jpg') line = '你好' color = (0, 255, 0) # Green pos = (3, 3) text_size = 24 # ft = put_chinese_text('wqy-zenhei.ttc') ft = ft2.put_chinese_text('msyh.ttf') image = ft.draw_text(img, pos, line, text_size, color) name = u'图片展示' cv2.imshow(name, image) cv2.waitKey(0)
try: contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img_edge2, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) except ValueError: image, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img_edge2, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) contours = [cnt for cnt in contours if cv2.contourArea(cnt) > Min_Area] car_contours = [] for cnt in contours: rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt) area_width, area_height = rect[1] if area_width < area_height: area_width, area_height = area_height, area_width wh_ratio = area_width / area_height #print(wh_ratio) #要求矩形区域长宽比在2到5.5之间,2到5.5是车牌的长宽比,其余的矩形排除 if wh_ratio > 2 and wh_ratio < 5.5: car_contours.append(rect) box = cv2.boxPoints(rect) box = np.int0(box) for rect in car_contours: if rect[2] > -1 and rect[2] < 1:#创造角度,使得左、高、右、低拿到正确的值 angle = 1 else: angle = rect[2] rect = (rect[0], (rect[1][0]+5, rect[1][1]+5), angle)#扩大范围,避免车牌边缘被排除 box = cv2.boxPoints(rect) heigth_point = right_point = [0, 0] left_point = low_point = [pic_width, pic_hight] for point in box: if left_point[0] > point[0]: left_point = point if low_point[1] > point[1]: low_point = point if heigth_point[1] < point[1]: heigth_point = point if right_point[0] < point[0]: right_point = point if left_point[1] <= right_point[1]:#正角度 new_right_point = [right_point[0], heigth_point[1]] pts2 = np.float32([left_point, heigth_point, new_right_point])#字符只是高度需要改变 pts1 = np.float32([left_point, heigth_point, right_point]) M = cv2.getAffineTransform(pts1, pts2) dst = cv2.warpAffine(oldimg, M, (pic_width, pic_hight)) point_limit(new_right_point) point_limit(heigth_point) point_limit(left_point) card_img = dst[int(left_point[1]):int(heigth_point[1]), int(left_point[0]):int(new_right_point[0])] card_imgs.append(card_img) elif left_point[1] > right_point[1]:#负角度 new_left_point = [left_point[0], heigth_point[1]] pts2 = np.float32([new_left_point, heigth_point, right_point])#字符只是高度需要改变 pts1 = np.float32([left_point, heigth_point, right_point]) M = cv2.getAffineTransform(pts1, pts2) dst = cv2.warpAffine(oldimg, M, (pic_width, pic_hight)) point_limit(right_point) point_limit(heigth_point) point_limit(new_left_point) card_img = dst[int(right_point[1]):int(heigth_point[1]), int(new_left_point[0]):int(right_point[0])] card_imgs.append(card_img) colors = [] for card_index,card_img in enumerate(card_imgs): green = yello = blue = black = white = 0 card_img_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(card_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV) #有转换失败的可能,原因来自于上面矫正矩形出错 if card_img_hsv is None: continue row_num, col_num= card_img_hsv.shape[:2] card_img_count = row_num * col_num for i in range(row_num): for j in range(col_num): H = card_img_hsv.item(i, j, 0) S = card_img_hsv.item(i, j, 1) V = card_img_hsv.item(i, j, 2) if 11 < H <= 34 and S > 34:#图片分辨率调整 yello += 1 elif 35 < H <= 99 and S > 34:#图片分辨率调整 green += 1 elif 99 < H <= 124 and S > 34:#图片分辨率调整 blue += 1 if 0 < H <180 and 0 < S < 255 and 0 < V < 46: black += 1 elif 0 < H <180 and 0 < S < 43 and 221 < V < 225: white += 1 color = "no" limit1 = limit2 = 0 if yello*2 >= card_img_count: color = "yello" limit1 = 11 limit2 = 34#有的图片有色偏偏绿 elif green*2 >= card_img_count: color = "green" limit1 = 35 limit2 = 99 elif blue*2 >= card_img_count: color = "blue" limit1 = 100 limit2 = 124#有的图片有色偏偏紫 elif black + white >= card_img_count*0.7:#TODO color = "bw" print(color) colors.append(color) print(blue, green, yello, black, white, card_img_count) cv2.imshow("color", card_img) cv2.waitKey(1110) if limit1 == 0: continue #以上为确定车牌颜色 #以下为根据车牌颜色再定位,缩小边缘非车牌边界 xl, xr, yh, yl = self.accurate_place(card_img_hsv, limit1, limit2, color) if yl == yh and xl == xr: continue need_accurate = False if yl >= yh: yl = 0 yh = row_num need_accurate = True if xl >= xr: xl = 0 xr = col_num need_accurate = True card_imgs[card_index] = card_img[yl:yh, xl:xr] if color != "green" or yl < (yh-yl)//4 else card_img[yl-(yh-yl)//4:yh, xl:xr] if need_accurate:#可能x或y方向未缩小,需要再试一次 card_img = card_imgs[card_index] card_img_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(card_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV) xl, xr, yh, yl = self.accurate_place(card_img_hsv, limit1, limit2, color) print('size', xl,xr,yh,yl) if yl == yh and xl == xr: continue if yl >= yh: yl = 0 yh = row_num if xl >= xr: xl = 0 xr = col_num card_imgs[card_index] = card_img[yl:yh, xl:xr] if color != "green" or yl < (yh-yl)//4 else card_img[yl-(yh-yl)//4:yh, xl:xr] 
核心部分来了,详解一下:
predict_result = [] roi = None card_color = None for i, color in enumerate(colors): if color in ("blue", "yello", "green"): card_img = card_imgs[i] gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(card_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) #黄、绿车牌字符比背景暗、与蓝车牌刚好相反,所以黄、绿车牌需要反向 if color == "green" or color == "yello": gray_img = cv2.bitwise_not(gray_img) ret, gray_img = cv2.threshold(gray_img, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY + cv2.THRESH_OTSU) #查找水平直方图波峰 x_histogram = np.sum(gray_img, axis=1) x_min = np.min(x_histogram) x_average = np.sum(x_histogram)/x_histogram.shape[0] x_threshold = (x_min + x_average)/2 wave_peaks = find_waves(x_threshold, x_histogram) if len(wave_peaks) == 0: print("peak less 0:") continue #认为水平方向,最大的波峰为车牌区域 wave = max(wave_peaks, key=lambda x:x[1]-x[0]) gray_img = gray_img[wave[0]:wave[1]] #查找垂直直方图波峰 row_num, col_num= gray_img.shape[:2] #去掉车牌上下边缘1个像素,避免白边影响阈值判断 gray_img = gray_img[1:row_num-1] y_histogram = np.sum(gray_img, axis=0) y_min = np.min(y_histogram) y_average = np.sum(y_histogram)/y_histogram.shape[0] y_threshold = (y_min + y_average)/5#U和0要求阈值偏小,否则U和0会被分成两半 wave_peaks = find_waves(y_threshold, y_histogram) #for wave in wave_peaks: # cv2.line(card_img, pt1=(wave[0], 5), pt2=(wave[1], 5), color=(0, 0, 255), thickness=2) #车牌字符数应大于6 if len(wave_peaks) <= 6: print("peak less 1:", len(wave_peaks)) continue wave = max(wave_peaks, key=lambda x:x[1]-x[0]) max_wave_dis = wave[1] - wave[0] #判断是否是左侧车牌边缘 if wave_peaks[0][1] - wave_peaks[0][0] < max_wave_dis/3 and wave_peaks[0][0] == 0: wave_peaks.pop(0) #组合分离汉字 cur_dis = 0 for i,wave in enumerate(wave_peaks): if wave[1] - wave[0] + cur_dis > max_wave_dis * 0.6: break else: cur_dis += wave[1] - wave[0] if i > 0: wave = (wave_peaks[0][0], wave_peaks[i][1]) wave_peaks = wave_peaks[i+1:] wave_peaks.insert(0, wave) #去除车牌上的分隔点 point = wave_peaks[2] if point[1] - point[0] < max_wave_dis/3: point_img = gray_img[:,point[0]:point[1]] if np.mean(point_img) < 255/5: wave_peaks.pop(2) if len(wave_peaks) <= 6: print("peak less 2:", len(wave_peaks)) continue part_cards = seperate_card(gray_img, wave_peaks) for i, part_card in enumerate(part_cards): #可能是固定车牌的铆钉 if np.mean(part_card) < 255/5: print("a point") continue part_card_old = part_card w = abs(part_card.shape[1] - SZ)//2 part_card = cv2.copyMakeBorder(part_card, 0, 0, w, w, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value = [0,0,0]) part_card = cv2.resize(part_card, (SZ, SZ), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) #part_card = deskew(part_card) part_card = preprocess_hog([part_card]) if i == 0: resp = self.modelchinese.predict(part_card) charactor = provinces[int(resp[0]) - PROVINCE_START] else: resp = self.model.predict(part_card) charactor = chr(resp[0]) #判断最后一个数是否是车牌边缘,假设车牌边缘被认为是1 if charactor == "1" and i == len(part_cards)-1: if part_card_old.shape[0]/part_card_old.shape[1] >= 7:#1太细,认为是边缘 continue predict_result.append(charactor) roi = card_img card_color = color break return predict_result, roi, card_color#识别到的字符、定位的车牌图像、车牌颜色 gray_img = cv2.bitwise_not(gray_img) def find_waves(threshold, histogram): up_point = -1#上升点 is_peak = False if histogram[0] > threshold: up_point = 0 is_peak = True wave_peaks = [] for i,x in enumerate(histogram): if is_peak and x < threshold: if i - up_point > 2: is_peak = False wave_peaks.append((up_point, i)) elif not is_peak and x >= threshold: is_peak = True up_point = i if is_peak and up_point != -1 and i - up_point > 4: wave_peaks.append((up_point, i)) return wave_peaks def seperate_card(img, waves): part_cards = [] for wave in waves: part_cards.append(img[:, wave[0]:wave[1]]) return part_cards def deskew(img): m = cv2.moments(img) if abs(m['mu02']) < 1e-2: return img.copy() skew = m['mu11']/m['mu02'] M = np.float32([[1, skew, -0.5*SZ*skew], [0, 1, 0]]) img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (SZ, SZ), flags=cv2.WARP_INVERSE_MAP | cv2.INTER_LINEAR) return img m = cv2.moments(img) #车牌字符数应大于6 if len(wave_peaks) <= 6: print("peak less 1:", len(wave_peaks)) continue wave = max(wave_peaks, key=lambda x:x[1]-x[0]) max_wave_dis = wave[1] - wave[0] #判断是否是左侧车牌边缘 if wave_peaks[0][1] - wave_peaks[0][0] < max_wave_dis/3 and wave_peaks[0][0] == 0: wave_peaks.pop(0) #组合分离汉字 cur_dis = 0 for i,wave in enumerate(wave_peaks): if wave[1] - wave[0] + cur_dis > max_wave_dis * 0.6: break else: cur_dis += wave[1] - wave[0] if i > 0: wave = (wave_peaks[0][0], wave_peaks[i][1]) wave_peaks = wave_peaks[i+1:] wave_peaks.insert(0, wave) #去除车牌上的分隔点 point = wave_peaks[2] if point[1] - point[0] < max_wave_dis/3: point_img = gray_img[:,point[0]:point[1]] if np.mean(point_img) < 255/5: wave_peaks.pop(2) if len(wave_peaks) <= 6: print("peak less 2:", len(wave_peaks)) continue part_cards = seperate_card(gray_img, wave_peaks) for i, part_card in enumerate(part_cards): #可能是固定车牌的铆钉 if np.mean(part_card) < 255/5: print("a point") continue part_card_old = part_card w = abs(part_card.shape[1] - SZ)//2 part_card = cv2.copyMakeBorder(part_card, 0, 0, w, w, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value = [0,0,0]) part_card = cv2.resize(part_card, (SZ, SZ), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) #part_card = deskew(part_card) part_card = preprocess_hog([part_card]) if i == 0: resp = self.modelchinese.predict(part_card) charactor = provinces[int(resp[0]) - PROVINCE_START] else: resp = self.model.predict(part_card) charactor = chr(resp[0]) #判断最后一个数是否是车牌边缘,假设车牌边缘被认为是1 if charactor == "1" and i == len(part_cards)-1: if part_card_old.shape[0]/part_card_old.shape[1] >= 7:#1太细,认为是边缘 continue predict_result.append(charactor) roi = card_img card_color = color break return predict_result, roi, card_color if __name__ == '__main__': c = CardPredictor() c.train_svm() r, roi, color = c.predict("test//car7.jpg") print(r, roi.shape[0],roi.shape[1],roi.shape[2]) img = cv2.imread("test//car7.jpg") img = cv2.resize(img,(480,640),interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) r = ','.join(r) r = r.replace(',', '') print(r) from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont cv2img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # cv2和PIL中颜色的hex码的储存顺序不同 pilimg = Image.fromarray(cv2img) # PIL图片上打印汉字 draw = ImageDraw.Draw(pilimg) # 图片上打印 font = ImageFont.truetype("simhei.ttf", 30, encoding="utf-8") # 参数1:字体文件路径,参数2:字体大小 draw.text((0, 0), r, (255, 0, 0), font=font) # 参数1:打印坐标,参数2:文本,参数3:字体颜色,参数4:字体 # PIL图片转cv2 图片 cv2charimg = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(pilimg), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) # cv2.imshow("图片", cv2charimg) # 汉字窗口标题显示乱码 cv2.imshow("photo", cv2charimg) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows() OPENCV的SVM的SVC训练模型——>OpenCv进行图像采集/控制摄像头——>图像预处理(二值化操作,边缘计算等)——>定位车牌位置,并正放置处理——>确定车牌颜色——>根据车牌颜色再定位,缩小边缘非车牌边界——>以下为识别车牌中的字符——>返回结果——>最后ptrdict返回识别到的字符、定位的车牌图像、车牌颜色——>结果显示,并使用PIL方法显示中文
最后我想说明的是,根据我找bug的能力,已经发现一堆bug,但是无可否认,这个机器学习项目已经写的很棒了,至少我短期不能达到这个效果,不过写出来还是没有太大困难,逻辑在,做就完了!另外,程序基于机器学习的SVM算法问题,以及在数据预处理上的优化问题 ,还是很欠缺的,最大的问题就是准确率问题,以及欠拟合问题,这两者是我这个项目的问题,换成深度学习会好很多!


本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)