水平有限,有误的地方望批评指正。 文章从两大方面讲解,1、介绍,2、源码解析 String类代表了java中的字符串, 一、String介绍 1、不可变类,线程安全。 不可变类在java语言中使用final关键字实现,final有三个作用,简单的说修饰的类不可继承,方法不可重写,变量不可修改。而String类和存储字符数据的Char数组就是用final修饰的,因此string类不可继承,内部数据(char数组)不能修改,对String进行替换,裁剪,连接都是新生成一个String对象,因此String是不可变类,不可变类都是线程安全的,最典型的就是JAVA中的包装类Integer,Long等。为什么不可变类是线程安全的呢?因为String对象是无状态对象,无状态对象可以理解为状态不能改变的对象,这里的状态也可以理解为对象里的数据。 2、可共享 jdk7运行时常量池存储在方法区,也就是永久代(hotspot),jdk8永久代被移除,运行时常量池存储在本地内存的元空间中,运行时常量池存储了字符串常量的引用,字符串常量存储在堆中。java就是使用常量池来实现字符串共享的,下面我们看下例子 结果是一个true,一个false。a和b都指向了常量池中的引用,因此他们的地址相同的,a==b也就为true,而c指向的是在堆上新创建的对象的引用,和a不是指向同一个字符串地址,因此a==c为false,javap对应的指令 大家查看划线的几个地方,从上往下第一处,第二处,第四处都是从常量池获取字符传test的引用,而第三处是new返回的引用,所以a和b地址一样,a,b和c的地址不一样。 3、简单高效 程序中最常见的就是字符串拼接操作,java中可以直接使用+运算符来表示字符串拼接,我们看以下代码。 查看编译后的指令 1、创建一个StringBuilder对象 2、调用StringBuilder的构造函数 3、3,4,5步骤都是调用StringBuilder的append方法将s1,s2,和”c”拼接起来。 结论:字符串+运算被java编译器编译后变成新建一个StringBuilder对象,然后每个+会编译成append方法,因此我们在一般情况下可以直接使用+拼接字符串,java为什么要这么做呢,就是因为性能,如果不使用StringBuilder拼接过程会产生很多中间String对象。当然有些情况下需要显式使用StringBuilder,看下面代码。 javap查看指令 1、1弹出栈顶两个元素进行比较,如果第二个元素大于等于第一个元素就跳转到36代码处,36代码处就是跳出for循环输出结果System.out的地方,栈中弹出第一个元素是10第二个是常量i(先入后出),说明i大于等于10则循环结束。 2、2和3表示创建StringBuilder对象,4,5表示调用append拼接s1和i 3、6表示将拼接后的结果存储在索引为1的局部变量中 4、7表示将局部变量索引为2的变量加1也就是1 5、8表示跳转到指令5处,进行下一次比较和循环 结论:分析指令后我们发现for循环中使用+进行字符串拼接,编译器编译后每次都会在for循环内部生成一个StringBuilder对象,然后调用append拼接字符串,如果for循环过大会产生大量StringBuilder对象,引起性能问题,所以我们在循环外新建StringBuilder,循环内调用append操作,代码比较简单我们就不做展示了。 二、源码解析 1、String实现了Serializable,Comparable<String>,CharSequence代表String是可序列化,可比较,字符序列。 2、主要属性 char value[] 字符存储数组 private int hash hash值 static final Comparator<String> CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER 忽略大小写的比较器 3、常用方法 1、如果h不为0或者value的长度为0则直接返回h,h不为0的情况说明h已经被计算过直接返回,所以hashCode只会计算一次。 2、遍历char数组中的每个字符值加上h*31,数组中的每个元素都参加运算让结果更加准确,h*31使hashcode值更加分散,乘以31也可以被优化成位数操作,计算效率更快。 3、给h赋值后返回 1、验证参数是否正确 1、last,lasto都指向参数索引位置。 2、parse(format)解析字符串,将分割后的普通字符串和格式化字符串添加到FormatString[]中,FormatString是个接口,有两个实现类FixedString代表普通字符串,索引index为-2,FormatSpecifier代表格式化字符,用来格式化参数,index有三种取值,0代表正常索引,也就是不指定索引位置的格式化字符,例如%s,%d,-1代表相对位置,取last位置的参数使用此格式化字符进行格式化,例如%<s,%<d, default代表显式指定参数索引的参数,例如%1$s,%2$s 3、遍历FormatString,index为-2表示普通字符串,则直接使用Formatter里的属性a(StringBuilder)进行拼接 4、index为-1,格式化字符使用相对位置,则使用上一个索引last的参数调用print进行格式化,格式化后的字符串使用属性a拼接。 5、index为0,格式化字符使用顺序位置,lasto加1,指向当前位置的后一个参数,last赋值,对下一个位置字符串调用print格式化后,使用a拼接 6、default,格式化字符使用指定参数位置,使用index-1指向的参数调用print格式化,格式化后用a拼接 7、返回a.toString 1、如果字符串参数长度为0,直接返回当前字符串。 2、Arrays.copyOf创建一个大小为当前字符串长度加上参数字符串长度的数组,包含value的值,方法内部是新建一个大小为len+otherLen的数组,然后调用System.arraycopy将value数组的内容复制到新建的数组中,并返回新数组,System.arraycopy是本地方法,由c,c++提供更高效的实现。 3、将Str字符的数组数据放入新数组len开头到len+Str.length处,内部也是调用System.arraycopy。 4、新建字符串,构造参数为新数组buf。 1、判断regrex是否是一个字符的字符串,.并且不是$|()[{^?*+\字符之一,或者含有两个字符的字符串第一个字符是反斜杠,第二个字符不是ascll数字或字母,否则采用正则表达式处理 2、off表示截取起始位置,next字符匹配的位置,limited是否有分隔字符串数量的限制 3、调用while循环,寻找字符匹配的位置,如果到达分隔数量的限制,直接将剩余字符串添加到list中,否则截取off到next的字符串,也就是起始位置或上一个分隔符到当前分隔符的字符串。 3、如果off为0,说明没有匹配的字符,直接返回字符串 4、如果没有分隔数量的限制或者没有到达分隔数量的限制则添加剩余字符串 5、如果没有分隔数量的限制则去除尾部空字符串,4步骤有可能添加空字符串 6、字符串列表转为字符串数组后并返回。 1、如果两个字符相等直接返回当前字符串 2、找到第一个oldChar和newChar相等的位置i,新建char数组将小于i的字符放入新数组中 3、从i开始遍历,如果i下标的字符和oldChar相等,则新数组下标i赋值newChar,否则新数组下标赋值原来的字符。 4、返回新建的String,参数数组为新建的buf. 1、判断参数是否合法 2、直接调用String的构造函数创建新字符串,构造函数中使用Arrays.copyOfRange复制数据。 1、第一个while循环计算索引从0开始第一个字符不为空格的索引 2、第二个while循环计算索引从len开始第一个不为空格的索引 3、存在空格则调用subString返回截取的去掉前后空格的字符串,否则返回当前字符串。 其他的方法代码比较简单,就不再赘述了,大家有时间可以自己看一下。 下篇文章给大家讲解StringBuilder和StringBuffer
public static void main(String[] args) { String a = "test"; String b = "test"; System.out.println(a == b); String c = new String("test"); System.out.println(a == c); }
public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "a"; String s2 = "b"; String s3 = s1 + s2 + "c"; System.out.println(s3); }
public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "a"; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { s1 = s1 + i; } System.out.println(s1); }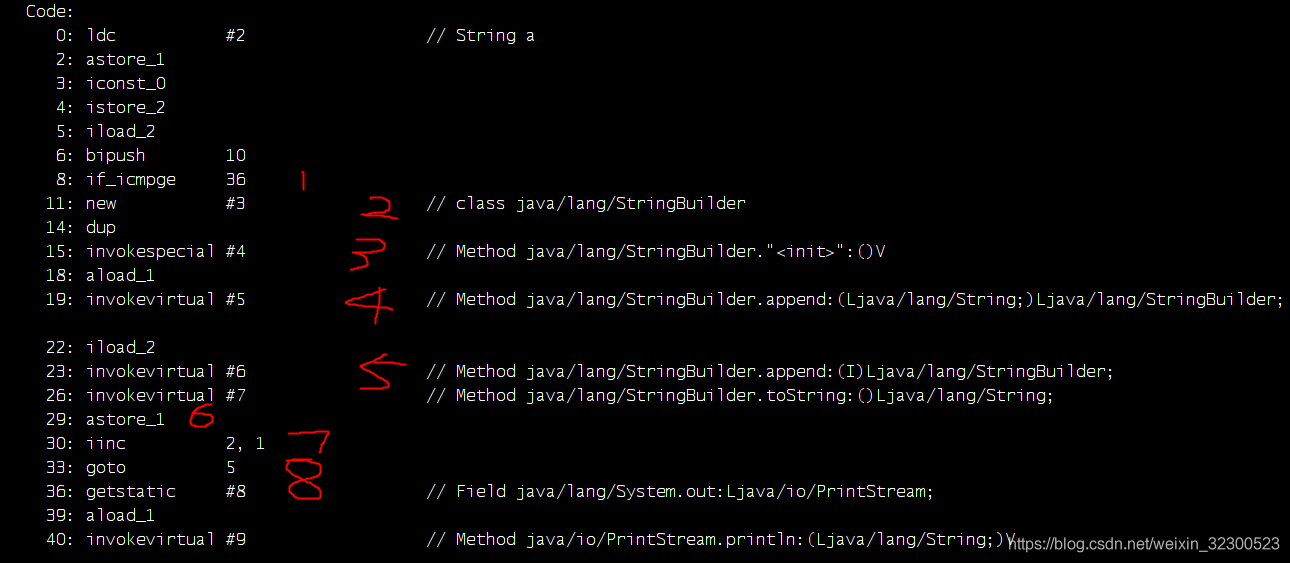
int hashCode() 计算对象的hashcode
public int hashCode() { int h = hash; if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) { //1 char val[] = value; for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) { //2 h = 31 * h + val[i]; } hash = h; //3 } return h; //3 }
static String join(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence... elements) elements使用delimiter分隔开拼接后返回
public static String join(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence... elements) { Objects.requireNonNull(delimiter); //1 Objects.requireNonNull(elements); //1 // Number of elements not likely worth Arrays.stream overhead. StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(delimiter); //2 for (CharSequence cs: elements) { //3 joiner.add(cs); } return joiner.toString(); //4 }
2、创建分隔符为delimiter的StringJoiner
3、遍历可变长字符串参数,对每个字符串调用joiner.add,joiner.add内部由一个StringBuilder的value属性,每次add就会使用value添加分隔符然后再添加字符串,value为空则添加前缀再添加字符串,此处无前缀。
4、调用joiner.toString()返回,如果没有后缀则返回value.toString,否则添加后缀后再返回toString,此处无后缀
static String format(String format, Object... args)
public Formatter format(Locale l, String format, Object ... args) { ensureOpen(); // index of last argument referenced int last = -1; //1 // last ordinary index int lasto = -1; //1 FormatString[] fsa = parse(format); //2 for (int i = 0; i < fsa.length; i++) { FormatString fs = fsa[i]; int index = fs.index(); try { switch (index) { case -2: // fixed string, "%n", or "%%" //3 fs.print(null, l); break; case -1: // relative index //4 if (last < 0 || (args != null && last > args.length - 1)) throw new MissingFormatArgumentException(fs.toString()); fs.print((args == null ? null : args[last]), l); break; case 0: // ordinary index //5 lasto++; last = lasto; if (args != null && lasto > args.length - 1) throw new MissingFormatArgumentException(fs.toString()); fs.print((args == null ? null : args[lasto]), l); break; default: // explicit index //6 last = index - 1; if (args != null && last > args.length - 1) throw new MissingFormatArgumentException(fs.toString()); fs.print((args == null ? null : args[last]), l); break; } } catch (IOException x) { lastException = x; } } return this; //7 }
String concat(String str) 当前字符串拼接str返回拼接后的字符串
public String concat(String str) { int otherLen = str.length(); if (otherLen == 0) { //1 return this; } int len = value.length; char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen); //2 str.getChars(buf, len); //3 return new String(buf, true); //4 }
String[] split(String regex, int limit) 根据regrex分隔字符串,limit为分隔字符串数量的限制
public String[] split(String regex, int limit) { /* fastpath if the regex is a (1)one-char String and this character is not one of the RegEx's meta characters ".$|()[{^?*+\", or (2)two-char String and the first char is the backslash and the second is not the ascii digit or ascii letter. */ char ch = 0; if (((regex.value.length == 1 && ".$|()[{^?*+\".indexOf(ch = regex.charAt(0)) == -1) || (regex.length() == 2 && regex.charAt(0) == '\' && (((ch = regex.charAt(1))-'0')|('9'-ch)) < 0 && ((ch-'a')|('z'-ch)) < 0 && ((ch-'A')|('Z'-ch)) < 0)) && (ch < Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE || ch > Character.MAX_LOW_SURROGATE)) //1 { int off = 0; //2 int next = 0; //2 boolean limited = limit > 0; ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); while ((next = indexOf(ch, off)) != -1) { //3 if (!limited || list.size() < limit - 1) { list.add(substring(off, next)); off = next + 1; } else { // last one //assert (list.size() == limit - 1); list.add(substring(off, value.length)); off = value.length; break; } } // If no match was found, return this if (off == 0) //4 return new String[]{this}; // Add remaining segment if (!limited || list.size() < limit) //5 list.add(substring(off, value.length)); // Construct result int resultSize = list.size(); if (limit == 0) { //6 while (resultSize > 0 && list.get(resultSize - 1).length() == 0) { resultSize--; } } String[] result = new String[resultSize]; return list.subList(0, resultSize).toArray(result); //7 } return Pattern.compile(regex).split(this, limit); //1 }
String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) 替换所有oldchar字符为newChar
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) { if (oldChar != newChar) { //1 int len = value.length; int i = -1; char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */ while (++i < len) { //2 if (val[i] == oldChar) { break; } } if (i < len) { char buf[] = new char[len]; for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { //3 buf[j] = val[j]; } while (i < len) { //4 char c = val[i]; buf[i] = (c == oldChar) ? newChar : c; i++; } return new String(buf, true); } } return this; }
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) 截取beginIndex到endIndex的字符串
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) { if (beginIndex < 0) { //1 throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex); } if (endIndex > value.length) { //1 throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex); } int subLen = endIndex - beginIndex; if (subLen < 0) { //1 throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen); } return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == value.length)) ? this : new String(value, beginIndex, subLen); //2 }
String trim() 清空字符串中前后的空格
public String trim() { int len = value.length; int st = 0; char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */ while ((st < len) && (val[st] <= ' ')) { //1 st++; } while ((st < len) && (val[len - 1] <= ' ')) { //2 len--; } return ((st > 0) || (len < value.length)) ? substring(st, len) : this; //3 }
public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset)
public boolean endsWith(String suffix)
lastIndexOf(int ch)
public int indexOf(int ch)
public boolean equals(Object anObject)
本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)