首先看一下SpringBoot的默认处理结果 这是页面响应 首先,SpringBoot所有的错误处理配置类ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 其中里面包含几个重要的组件 这个组件在发生请求之前就已经注入到Spring容器中了 首先进入的就是这个组件,通过调用registerErrorPages方法的**getPath()**方法最终得到错误页面路径, errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(errorPage);把/error路径下对应的错误页面注入到Servlet中,在请求访问异常的时候,会转发到 /error 路径下 errorHtml:用来响应浏览器请求时的错误信息 MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE:就代表了浏览器发起的请求,因为TEXT_HTML_VALUE = “text/html” error用来响应非浏览器请求时的错误信息,返回的是json格式 这也就解释了文章开头为什么用不同的方式请求会有不同的响应信息展示 源码如下 通过上面BasicErrorController判断是否为浏览器请求,如果非浏览器请求,就会调用error方法返回json信息;如果是浏览器请求,这时候就会进入到DefaultErrorViewResolver的**resolveErrorView()**方法 分两种情况:第一种可以通过模板引擎解析的页面;第二种模板引擎无法解析的页面 以上两种情况又各分为两种情况,可以精确匹配到的页面,比如404.html;另一种则是模糊匹配页面,比如4xx.html、5xx.html. 第一种:先说一下可以通过模板引擎解析的页面的精确匹配,首先这个页面是需要放在 /template/error/ 路径下的,当请求进入后,模板引擎会根据状态码解析错误页面,精确匹配到路径下的页面,功能实现就是这句this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName,this.applicationContext); 然后直接返回一个ModelAndView对象,如图,有页面则直接返回 第二种:模板引擎无法解析的页面和静态资源文件夹下也没有页面的情况,这时候this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName,this.applicationContext);会返回一个null,从而进入到 resolveResource() 方法,通过遍历静态资源文件位置获取匹配的页面,如果没有页面,则会返回系统默认的视图对象,截图展示 最后没有找到对应的页面,返回一个null,SpringBoot则会使用默认的页面展示,也就是文章开头那个图 views.put(Series.CLIENT_ERROR, “4xx”); 如果在精确匹配的情况下找不到页面,贼会使用模糊匹配的方式查找,就像这种4xx,5xx,截图在下面 上面是分析的精确匹配页面,接下来就看一下模糊匹配** META-INFO/resources/error/ 项目路径下/resources/error/ 项目路径下/static/error/ 项目路径下/public/error/ 源码如下: 类DefaultErrorAttributes中的 getErrorAttributes() 方法提供了默认的错误信息注入,可以获取到 getErrorAttributes()方法获取timestamp:时间戳 addStatus()方法获取status:状态码 addErrorDetails()方法获取exception:异常对象 addStackTrace()方法获取trace:堆栈信息(能力尚浅,仅是猜测) addExceptionErrorMessage()方法获取message:异常错误信息 addBindingResultErrorMessage()方法获取errors:JSR303校验信息 addPath()获取请求出错的路径path:错误路径 error/状态码,【将错误页面命名为 错误状态码.html 放在模板引擎文件夹里面的 error文件夹下】,发生此状态码的错误就会来到对应的页面;我们可以使用4xx和5xx作为错误页面的文件名来匹配这种类型的所有错误,精确优先(优先寻找精确的状态码.html) 获取定制页面的错误信息,在错误页面直接获取上面DefaultErrorAttributes提到的那些信息就可以 静态资源文件夹下找,第一部分错误处理机制中的第3节有提到 就是默认来到SpringBoot默认的错误提示页面 默认信息注入以及默认页面响应 先看一个默认的错误的json数据 timestamp:时间戳 status:状态码 error:错误提示 message:异常消息 path:路径 首先编写几个测试需要的类 这里就已经达到了自定义json格式数据,不再使用SpringBoot提供的格式,如图展示了页面和其他客户端数据样式 //自定义信息 首先说一下这一步实现自适应效果,原理还是使用的SpringBoot底层的BasicErrorController这个组件,因为它是自适应的 @RequestMapping(“KaTeX parse error: Expected ‘}’, got ‘EOF’ at end of input: …ver.error.path:{error.path:/error}}”) 因为我们是跳转到了 /error路径下,所以 BasicErrorController会去 /error路径下寻找页面;如果是其他客户端请求,就会返回json数据,这样就达到了自适应效果,BasicErrorController这个组件的具体讲解请参考SpringBoot错误处理机制的1.2节 可以看到这两个方法中都有一段共同的代码HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);,它的作用就是为了给解析视图提供状态码,通过下面的源码request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE)可以看出来,SpringBoot首先是通过request域对象中获取状态码,但是这里有一个参数RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE,这个参数的具体值就是javax.servlet.error.status_code 所以我们在自定义异常处理器时,需要手动指定状态码,否则不生效 request.setAttribute(“javax.servlet.error.status_code”,400); 到这里,我们已经可以做到了自定义异常处理器的自适应效果,但是还有一个问题,就是无论页面还是其他客户端展示的信息还是系统默认的,我们自定义的异常信息没有展示,接下来继续改善它 效果图如下 下面我们来说一下原理,从上面MyErrorAttributes这个类可以看出,它继承了DefaultErrorAttributes,是不是感觉很眼熟,它就是出现在SpringBoot错误处理机制的1.4节,不懂的小伙伴,可以往上翻一番。先看一段源码 看完源码后,小伙伴是不是又感觉好眼熟,对的,你的感觉没有错,SpringBoot错误处理机制的1.4节具体讲过,这里我们需要看的是这段代码 这里的 getErrorAttributes() 方法就是我们重写的那个方法,这个方法里面包含了这段代码 为我们返回了系统默认格式的异常信息集合,我们就是在这个基础上扩展自己定义的异常信息,所以就出现了这一小节开头的那段代码 Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options); 作用是调用父类的 getErrorAttributes() 方法,返回原生的异常信息集合 Map<String,Object> ext = (Map<String, Object>) webRequest.getAttribute(“ext”, 0); 添加自定义异常信息,首先获取到request域对象中自己添加的信息(request域对象信息是我们在2.2.2小节添加的request.setAttribute(“ext”,map);) 这里我们再说一下 webRequest.getAttribute(“ext”, 0);,第一个参数就不用解释了,获取域对象中封装的信息;那这个0的是用来干嘛的呢?看一下源码 我们自己写的这个类MyErrorAttributes继承自DefaultErrorAttributes,而DefaultErrorAttributes又实现了了RequestAttributes接口,所以,我们必须要给定第二个参数,这就出现了0,到这里我们应该就可以理解了,这个0就是用来确定request域对象的,这样我们就可以从request域对象中获取之前自定义的异常信息了。 到这里关于SpringBoot的错误处理机制以及自定义错误响应页面和自定义异常信息就说的差不多了,本人刚开始学,实在是能力有限,以上只是个人理解,如有写的不对的地方,敬请批评指正。
一、SpringBoot默认的错误处理机制

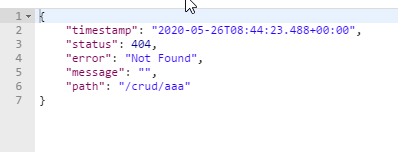
这是非页面响应
看到不同的响应信息,大家可能有疑惑“访问同一个地址,为什么展示效果却不一样呢?”,其实这跟SpringBoot的处理机制有关系,下面就简单讲解一下它的错误处理机制。@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET) @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class }) // Load before the main WebMvcAutoConfiguration so that the error View is available @AutoConfigureBefore(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class) @EnableConfigurationProperties({ ServerProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class }) public class ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration {DefaultErrorViewResolver 1、ErrorPageCustomizer:注册错误页面
@Bean public ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer(DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) { return new ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, dispatcherServletPath); } /** ErrorPageRegistry这个接口定义了在发生异常时该有哪些错误页面被添加 */ @FunctionalInterface public interface ErrorPageRegistry { /** * Adds error pages that will be used when handling exceptions. * 添加处理异常时将使用的错误页 * @param errorPages the error pages */ void addErrorPages(ErrorPage... errorPages); } @Override public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry) { ErrorPage errorPage = new ErrorPage( this.dispatcherServletPath.getRelativePath(this.properties.getError().getPath())); //添加处理异常时将使用的错误页 errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(errorPage); } public String getPath() { return this.path; } @Value("${error.path:/error}") private String path = "/error"; 2、BasicErrorController:SpringBoot统一异常处理Controller
/** * A String equivalent of {@link MediaType#TEXT_HTML}. */ public static final String TEXT_HTML_VALUE = "text/html"; //这个方法时用来响应浏览器请求时的错误信息 @RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); Map<String, Object> model = Collections .unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML))); response.setStatus(status.value()); ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model); return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model); } //这个方法时用来响应非浏览器请求时的错误信息 @RequestMapping public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) { HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) { return new ResponseEntity<>(status); } Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL)); return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status); } 3、DefaultErrorViewResolver:解析要跳转到哪个错误页面
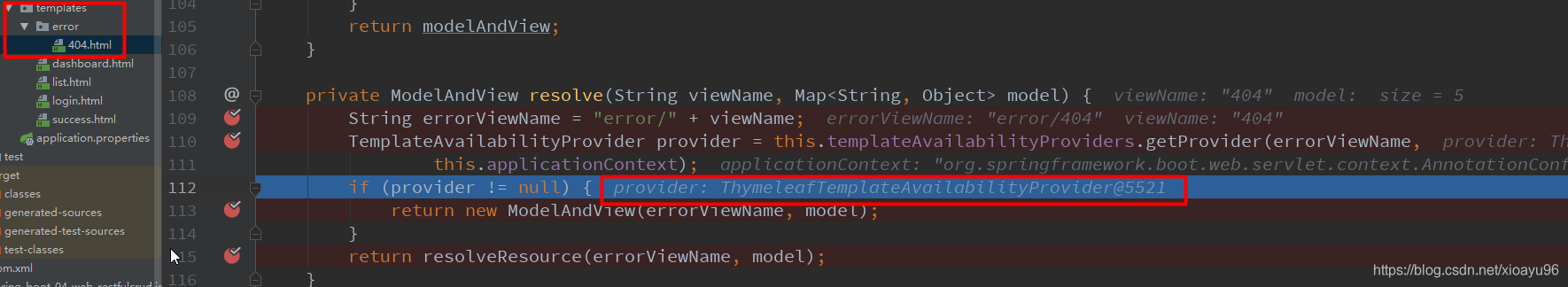
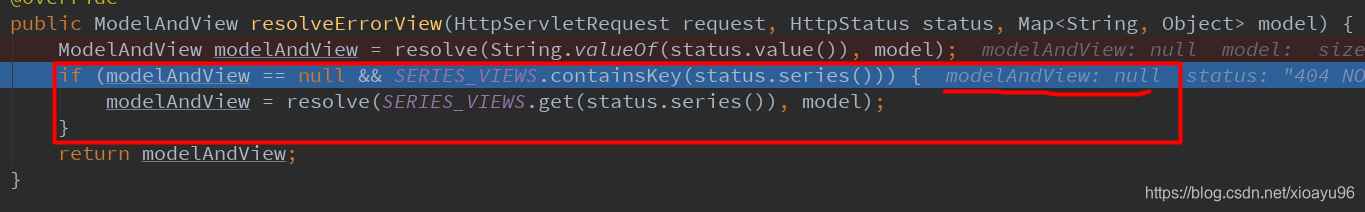
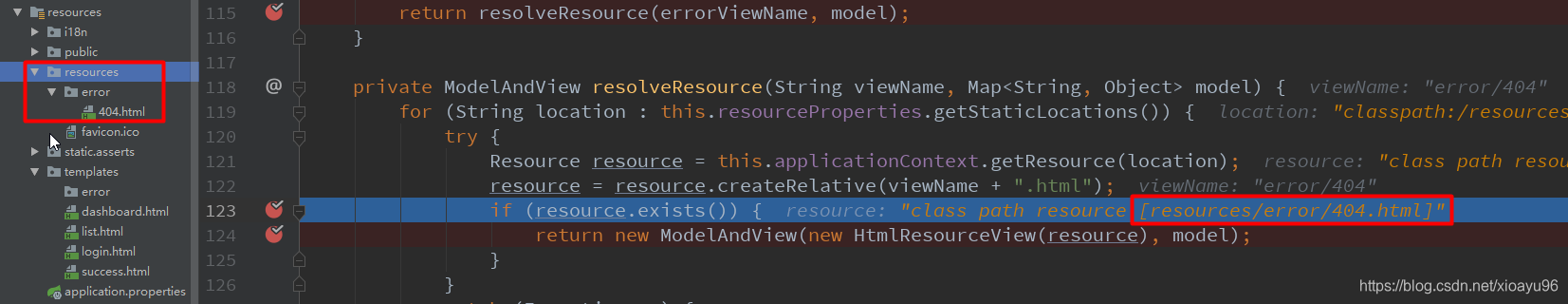
public class DefaultErrorViewResolver implements ErrorViewResolver, Ordered { static { Map<Series, String> views = new EnumMap<>(Series.class); views.put(Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "4xx"); views.put(Series.SERVER_ERROR, "5xx"); SERIES_VIEWS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(views); } @Override public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) { ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model); if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) { modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model); } return modelAndView; } private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) { String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName; TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext); if (provider != null) { return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model); } return resolveResource(errorViewName, model); } private ModelAndView resolveResource(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) { for (String location : this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()) { try { Resource resource = this.applicationContext.getResource(location); resource = resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html"); if (resource.exists()) { return new ModelAndView(new HtmlResourceView(resource), model); } } catch (Exception ex) { } } return null; } }

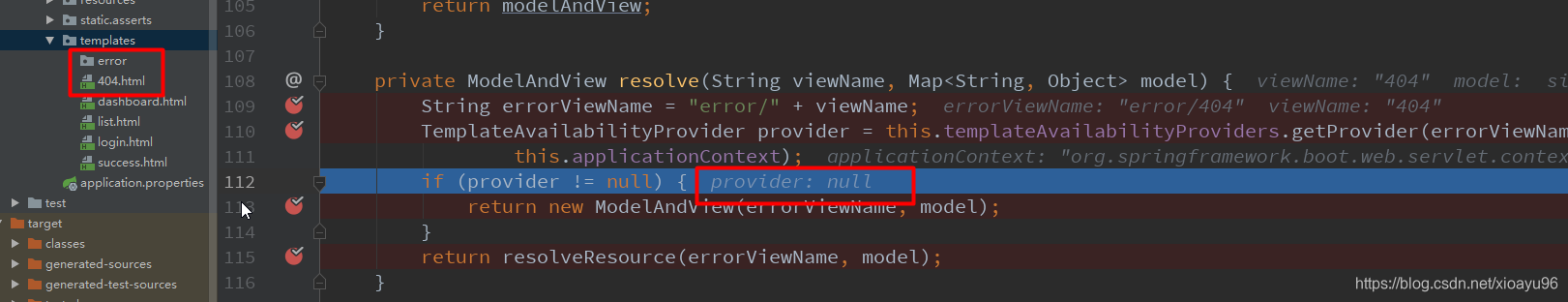
开始调用**resolveResource()方法遍历所有静态资源路径
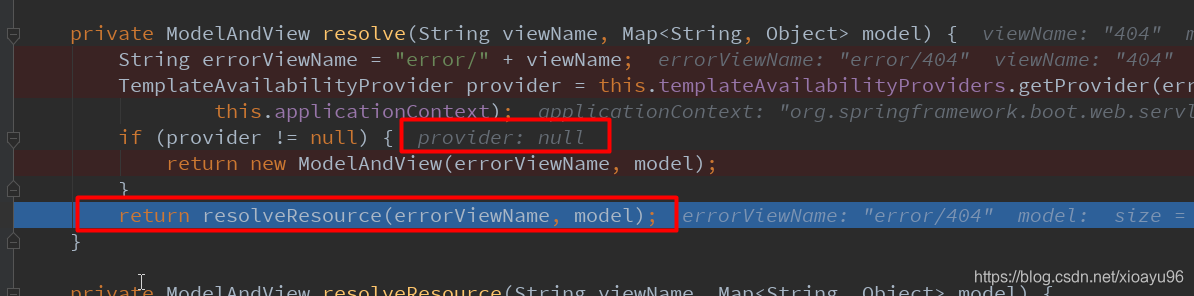
先找 META-INFO/resources/error/ 路径下有没有匹配的页面
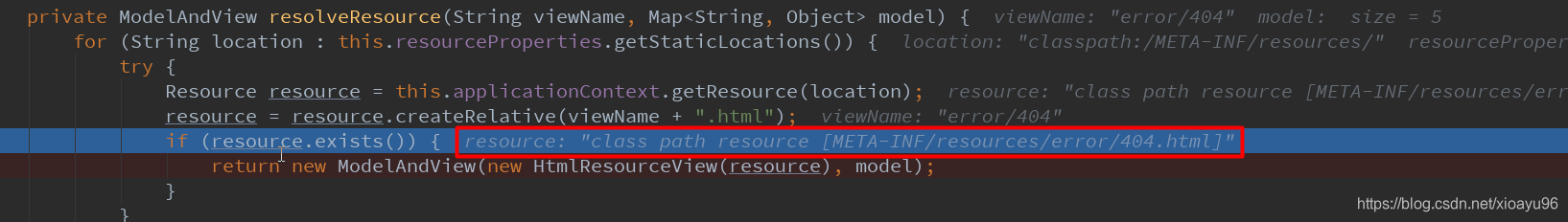
再找当前项目路径下/resources/error/下有没有匹配的页面
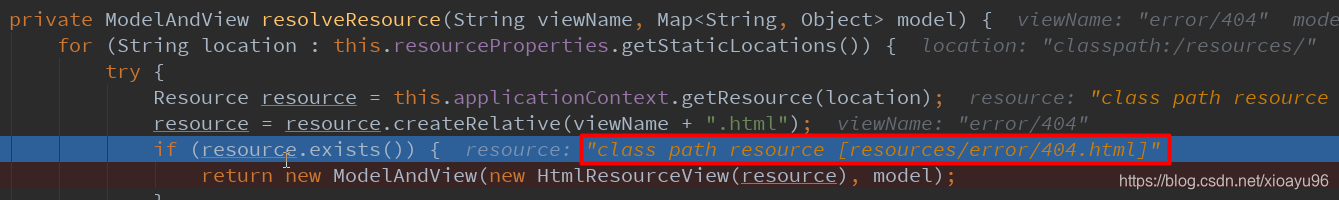
然后找当前项目路径下/static/error/下有没有匹配的页面
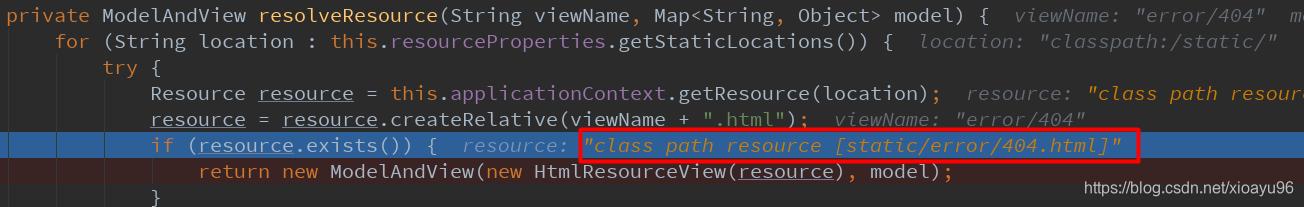
最后找当前项目路径下/public/error/**下有没有匹配的页面
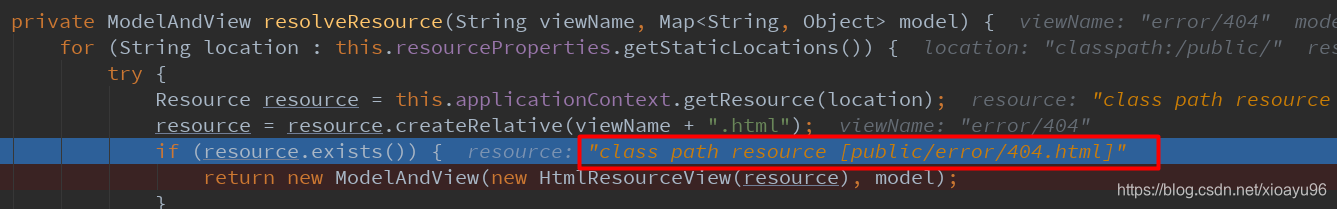
如果对应的静态资源文件下有页面则会直接匹配上,如图
通过分析,模板引擎只会解析/Template/error路径下的页面
这里还要说明一点内容: 源码定义了模糊匹配规则public class DefaultErrorViewResolver implements ErrorViewResolver, Ordered { static { Map<Series, String> views = new EnumMap<>(Series.class); views.put(Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "4xx"); views.put(Series.SERVER_ERROR, "5xx"); SERIES_VIEWS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(views); } }
views.put(Series.SERVER_ERROR, “5xx”);

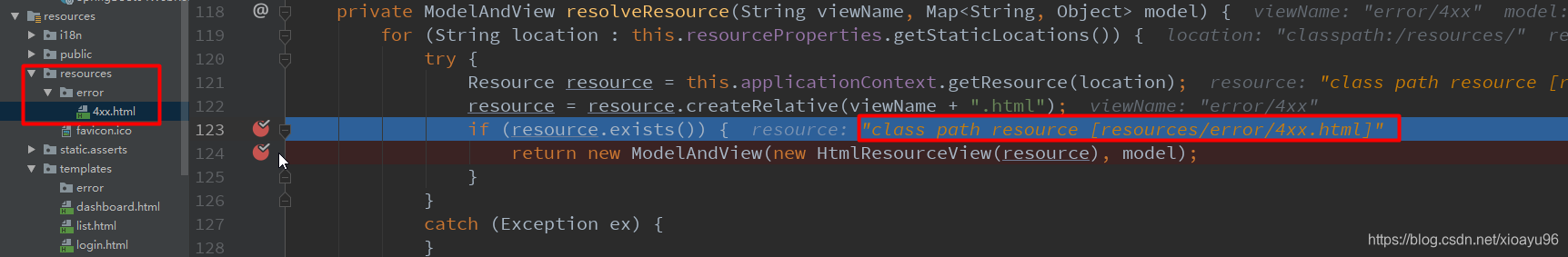
这时候把我选择把页面放在了 /resources/error/ 文件夹下,接下来的 循环遍历跟上面精确匹配逻辑一样,就不一一展示了,这里匹配到了;如果匹配不到返回一个null,SpringBoot则会使用默认的页面展示,也就是文章开头那个图
最终展示效果如图
通过上面遍历寻找页面可以得出一个结论:精确优先,寻找位置的优先级(从高到底),从源码也可以看出@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false) public class ResourceProperties { private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = { "classpath:/META-INF/resources/","classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" }; /** * Locations of static resources. Defaults to classpath:[/META-INF/resources/, * /resources/, /static/, /public/]. */ private String[] staticLocations = CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS; 4、DefaultErrorAttributes:注册了一个专门收集 error 发生时错误信息的bean,把错误信息注入到错误页面中
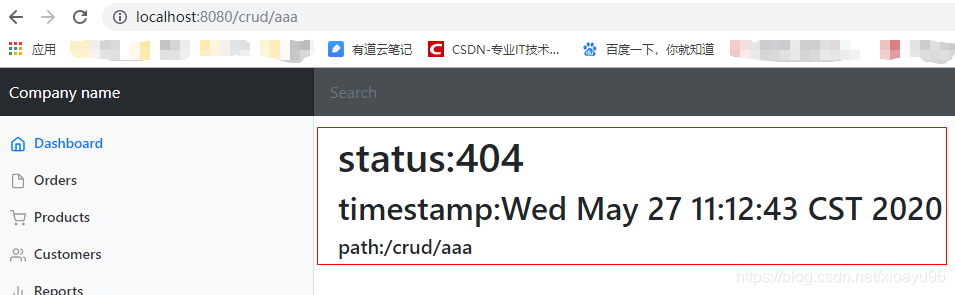
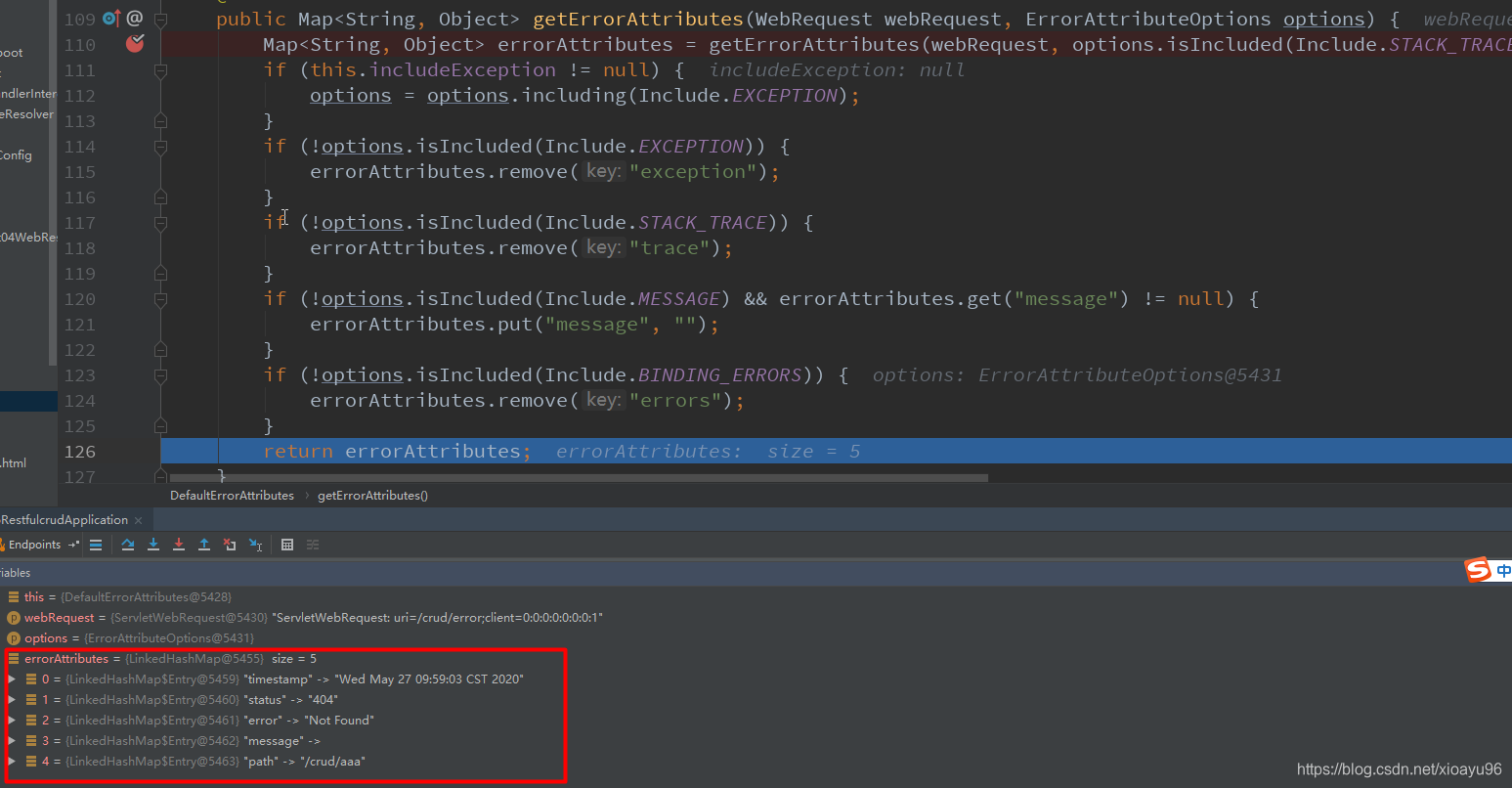
public class DefaultErrorAttributes implements ErrorAttributes, HandlerExceptionResolver, Ordered { @Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) { Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE)); return errorAttributes; } //时间戳 public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) { Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<>(); //获取时间戳 errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date()); addStatus(errorAttributes, webRequest); addErrorDetails(errorAttributes, webRequest, includeStackTrace); addPath(errorAttributes, webRequest); return errorAttributes; } //状态码 private void addStatus(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes, RequestAttributes requestAttributes) { Integer status = getAttribute(requestAttributes, RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE); if (status == null) { errorAttributes.put("status", 999); errorAttributes.put("error", "None"); return; } //获取状态码 errorAttributes.put("status", status); try { errorAttributes.put("error", HttpStatus.valueOf(status).getReasonPhrase()); } catch (Exception ex) { // Unable to obtain a reason errorAttributes.put("error", "Http Status " + status); } } //异常对象 private void addErrorDetails(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes, WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) { Throwable error = getError(webRequest); if (error != null) { while (error instanceof ServletException && error.getCause() != null) { error = error.getCause(); } //获取异常对象 errorAttributes.put("exception", error.getClass().getName()); if (includeStackTrace) { addStackTrace(errorAttributes, error); } } addErrorMessage(errorAttributes, webRequest, error); } //异常信息和JSR303校验信息的入口 private void addErrorMessage(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes, WebRequest webRequest, Throwable error) { BindingResult result = extractBindingResult(error); if (result == null) { addExceptionErrorMessage(errorAttributes, webRequest, error); } else { addBindingResultErrorMessage(errorAttributes, result); } } //异常错误信息 private void addExceptionErrorMessage(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes, WebRequest webRequest, Throwable error) { Object message = getAttribute(webRequest, RequestDispatcher.ERROR_MESSAGE); if (StringUtils.isEmpty(message) && error != null) { message = error.getMessage(); } if (StringUtils.isEmpty(message)) { message = "No message available"; } errorAttributes.put("message", message); } //JSR303数据校验错误信息 private void addBindingResultErrorMessage(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes, BindingResult result) { errorAttributes.put("message", "Validation failed for object='" + result.getObjectName() + "'. " + "Error count: " + result.getErrorCount()); errorAttributes.put("errors", result.getAllErrors()); } //目前能力尚浅,猜测是获取堆信息 private void addStackTrace(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes, Throwable error) { StringWriter stackTrace = new StringWriter(); error.printStackTrace(new PrintWriter(stackTrace)); stackTrace.flush(); errorAttributes.put("trace", stackTrace.toString()); } //请求路径 private void addPath(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes, RequestAttributes requestAttributes) { String path = getAttribute(requestAttributes, RequestDispatcher.ERROR_REQUEST_URI); if (path != null) { errorAttributes.put("path", path); } } } 二、自定义错误响应
1、定制错误页面
1)、有模板引擎的情况下;
2)、没有模板引擎(模板引擎找不到这个错误页面)
3)、以上都没有错误页面

2、定制错误的json数据
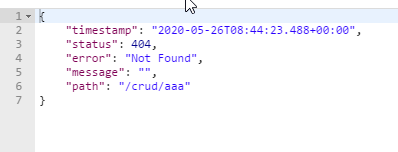
这里面只包含了
由上图可以看到error和message信息并没有展示出来,这是SpringBoot1.0和2.0的一点区别,2.0默认是关闭状态,需要在主配置文件配置一下
server.error.include-exception=true
server.error.include-message=always1)、自定义异常处理&返回定制json数据
/** * @PackageName : cn.rain.springboot.excepiton * @Created : 2020/5/27 * @Author : Rain * @Version : V1.0 * @Des : 自定义异常用来测试定制错误的json数据 */ public class MyException extends RuntimeException { public MyException() { super("用户名错误!"); } } /** * @PackageName : cn.rain.springboot.controller * @Created : 2020/5/27 * @Author : Rain * @Version : V1.0 * @Des : 自定义异常处理器,这里还达不到自适应效果,浏览器和其他客户端展示都是json格式数据 */ @ControllerAdvice public class MyexceptionHandler { @ResponseBody @ExceptionHandler(MyException.class) public Map<String,Object> handerException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request){ Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("msg1","我在学习SpringBoot自定义异常"); map.put("msg2","这是自定义异常信息:"+e.getMessage()); map.put("company","阿里爸爸"); return map; } }
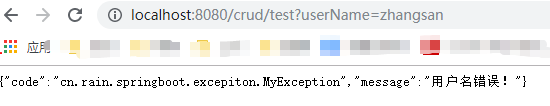
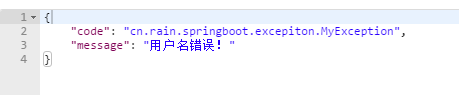
其实这样很不友好,无论从什么客户端发起请求,都会返回json格式数据,那怎么才可以达到自适应效果呢,往下看2)、转发到/error进行自适应响应效果处理
/** * @PackageName : cn.rain.springboot.controller * @Created : 2020/5/27 * @Author : Rain * @Version : V1.0 * @Des : 自定义异常处理器,这里在第1步的基础上做了修改,添加了状态码,改变了返回值 */ @ControllerAdvice public class MyexceptionHandler { @ExceptionHandler(MyException.class) public String handerException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request){ Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); //自定义信息 map.put("msg1","我在学习SpringBoot自定义异常"); map.put("msg2","这是自定义异常信息:"+e.getMessage()); map.put("company","阿里爸爸"); request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",400); request.setAttribute("ext",map); //转发到/error路径下,这里其实最终还是交给了SpringBoot来处理 return "forward:/error"; } } 
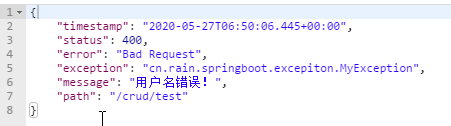
经过在第1步的基础上做了修改,添加了状态码,改变了返回值,这时候已经看出效果了,但是我们自己添加的信息好像没有展示出来
map.put(“code”,e.getClass());
map.put(“msg”,e.getMessage());@Controller @RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}") public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController { //下面这个两个方法就是SpringBoot为我们提供的 @RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); } @RequestMapping public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) { HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); } } protected HttpStatus getStatus(HttpServletRequest request) { Integer statusCode = (Integer) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE); if (statusCode == null) { return HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR; } try { return HttpStatus.valueOf(statusCode); } catch (Exception ex) { return HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR; } } public interface RequestDispatcher { public static final String ERROR_STATUS_CODE = "javax.servlet.error.status_code"; } 3)、将我们的定制数据携带到页面或者其他客户端
/** * @PackageName : cn.rain.springboot.component * @Created : 2020/5/27 * @Author : Rain * @Version : V1.0 * @Des : 自定义的ErrorAttributes,用来处理携带的自定义信息 */ @Configuration public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes { /** * 重写getErrorAttributes方法,这个方法也就是在SpringBoot默认的错误处理机制的1.4讲过的那个方法 * @param webRequest * @param options * @return */ @Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) { //调用父类的getErrorAttributes()方法,返回Map对象 Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options); //添加自定义异常信息,首先获取到request域对象中自己添加的信息,这是我们在自定义异常处理器手动添加进去的异常信息 //自定义信息 //map.put("msg1","我在学习SpringBoot自定义异常"); //map.put("msg2","这是自定义异常信息:"+e.getMessage()); //map.put("company","阿里爸爸"); Map<String,Object> ext = (Map<String, Object>) webRequest.getAttribute("ext", 0); errorAttributes.put("ext",ext); return errorAttributes; } }
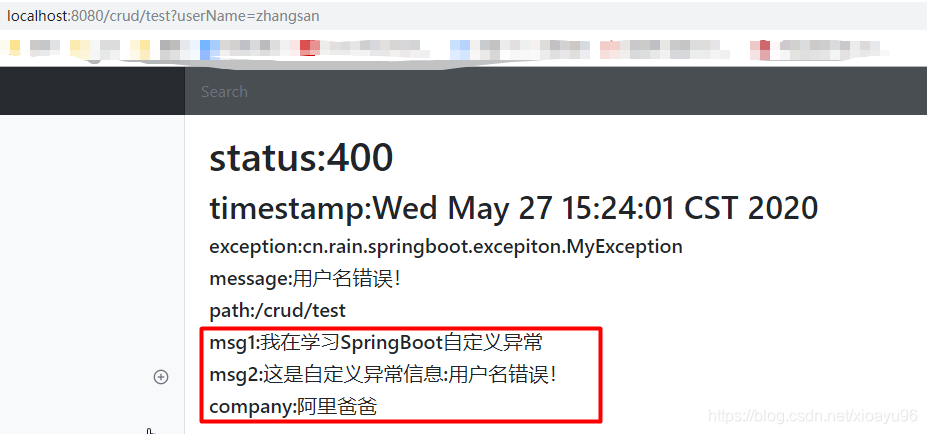
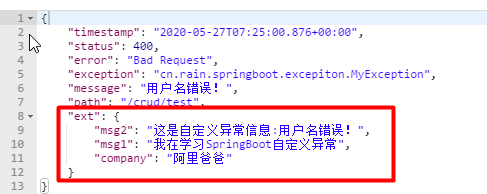
public class DefaultErrorAttributes implements ErrorAttributes, HandlerExceptionResolver, Ordered { @Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) { Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE)); if (this.includeException != null) { options = options.including(Include.EXCEPTION); } if (!options.isIncluded(Include.EXCEPTION)) { errorAttributes.remove("exception"); } if (!options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE)) { errorAttributes.remove("trace"); } if (!options.isIncluded(Include.MESSAGE) && errorAttributes.get("message") != null) { errorAttributes.put("message", ""); } if (!options.isIncluded(Include.BINDING_ERRORS)) { errorAttributes.remove("errors"); } return errorAttributes; } } public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) { Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE)); Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE)); /** * @PackageName : cn.rain.springboot.component * @Created : 2020/5/27 * @Author : Rain * @Version : V1.0 * @Des : 自定义的ErrorAttributes,用来处理携带的自定义信息 */ @Configuration public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes { /** * 重写getErrorAttributes方法,这个方法也就是在1.1.4讲过的那个方法 * @param webRequest * @param options * @return */ @Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) { //调用父类的getErrorAttributes()方法,返回Map对象 Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options); //添加自定义异常信息,首先获取到request域对象中自己添加的信息 Map<String,Object> ext = (Map<String, Object>) webRequest.getAttribute("ext", 0); errorAttributes.put("ext",ext); return errorAttributes; } } public interface RequestAttributes { /** * Constant that indicates request scope. */ int SCOPE_REQUEST = 0; @Nullable Object getAttribute(String name, int scope); }
本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)