英文教材第一章 1、2、3、4、5、9 An alternative to a LAN is simply a big timesharing system with terminals for all users. Give two advantages of a client-server system using a LAN. The performance of a client-server system is strongly influenced by two major network characteristics: the bandwidth of the network (that is, how many bits/sec it can transport) and the latency (that is, how many seconds it takes for the first bit to get from the client to the server). Give an example of a network that exhibits high bandwidth but also high latency. Then give an example of one that has both low bandwidth and low latency. Besides bandwidth and latency, what other parameter is needed to give a good characterization of the quality of service offered by a network used for (i) digitized voice traffic? (ii) video traffic? (iii) financial transaction traffic? A factor in the delay of a store-and-forward packet-switching system is how long it takes to store and forward a packet through a switch. If switching time is 10 μsec, is this likely to be a major factor in the response of a client-server system where the client is in New York and the server is in California? Assume the propagation speed in copper and fiber to be 2/3 the speed of light in vacuum. A client-server system uses a satellite network, with the satellite at a height of 40,000km. What is the best-case delay in response to a request? A disadvantage of a broadcast subnet is the capacity wasted when multiple hosts attempt to access the channel at the same time. As a simplistic example, suppose that time is divided into discrete slots, with each of the n hosts attempting to use the channel with probability p during each slot. What fraction of the slots will be wasted due to collisions? 英文版教材第一章 10,11,12,15,16,17,18,20,22,30 What are two reasons for using layered protocols? What is one possible disadvantage of using layered protocols? What is the principle difference between connectionless communication and connection-oriented communication? Give one example of a protocol that uses Two networks each provide reliable connection-oriented service. One of them offers a reliable byte stream and the other offers a reliable message stream. Are these identical? If so, why is the distinction made? If not, give an example of how they differ. In some networks, the data link layer handles transmission errors by requesting that damaged frames be retransmitted. If the probability of a frame’s being damaged is p, what is the mean number of transmissions required to send a frame? Assume that acknowledgements are never lost. Which of the OSI layers and TCP/IP layers handles each of the following: If the unit exchanged at the data link level is called a frame and the unit exchanged at the network level is called a packet, do frames encapsulate packets or do packets encapsulate frames? Explain your answer. A system has an n-layer protocol hierarchy. Applications generate messages of length M bytes. At each of the layers, an h-byte header is added. What fraction of the network bandwidth is filled with headers? What is the main difference between TCP and UDP? When a file is transferred between two computers, two acknowledgement strategies are possible. In the first one, the file is chopped up into packets, which are individually acknowledged by the receiver, but the file transfer as a whole is not acknowledged. In the second one, the packets are not acknowledged individually, but the entire file is acknowledged when it arrives. Discuss these two approaches. Suppose there is a change in the service (set of operations) provided by layer k. How does this impact services at layers k-1 and k+1?
考点:考查TDM和LAN的原理
答:①分时复用系统(TDM):
优点:无需竞争,负载大时冲突少,时延小;
缺点:不使用时浪费信道,负载小时时延较大(轮到自己才能发);
②LAN:
优点:负载轻时,竞争少,时延小;
缺点:负载重时,冲突多,时延大
考点:考查对网络性能指标带宽和时延以及有向传输介质特点的理解
答:①高带宽、高延迟:光纤(点到点,远距离-延迟高)
②低带宽、低延迟:双绞线(用于LAN,负载小,延迟小)
考点:考查对于除带宽和时延之外的其它网络性能指标的理解
答:(i)抖动
(ii)抖动
(iii)可靠性、安全性
考点:考查对3种时延的区别及计算
答:
v传=2/3×v光=2×108m/s
10微秒内传输的距离
d1=v传×t=2km
客户机到服务器的距离
d2=5000km≫2km
即使有多个交换机,交换时间也不会成为影响延迟的主要因素。
解题思路:考查传播时延的概念及计算
答:请求从客户机向服务器发送时,要经过卫星网络。从发送请求到响应请求的距离为
d=4×40000km=160000km。延迟时间
t=d/v光=533ms
考点:计网经典概率模型,求解平均概率
答:反向考虑问题,不发生冲突的情况为同一时间没有主机访问信道或只有一个主机访问信道,因此发生冲突的概率
p冲=1−Cn0(1−p)n−Cn1(1−p)n−1p=1−(1−p)n−np(1−p)n−1
考点:对层次通信模型特点的理解
答:原因:简化网络的设计和实现的难度;更改协议不会影响到高层或者低层的协议。
缺点:每层要加很多控制信息,增加了开销。
1 ) connectionless communication 2)connection-oriented communication.
考点:面向连接与无连接方式的区别及例子
答:面向连接(电路交换)对QoS有保证,无数据浪费信道
无连接(报文、分组交换)无需建立连接,每个分组加完整目的地址,接受端需按序重组。适合计算机网络的突发性。
例子:1)DNS、UDP 2)TCP
考点:报文流与字节流的区别
答:字节流:1字节占用1个序号(序号基于字节个数),为了保证可靠(每个字节正确传输)
报文流:多字节占用1个序号(序号基于报文个数)
考点:乘法概率模型的计算
答:发送1帧成功的概率为
1−p,则成功发送1帧需要
1/(1−p) 次传输
1 ) Dividing the transmitted bit stream into frames
2 ) Determining which route through the subnet to use.
考点:考查OSI与TCP/IP模型每层的功能
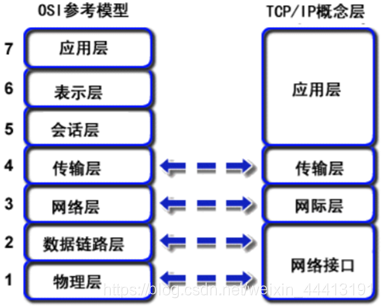
答:1)OSI:数据链路层 TCP/IP:网络接口层
2)OSI:网络层 TCP/IP:网际层 IP
考点:考查封装的概念
答:帧封装了分组。网络层在数据链路层的上层,在分组向下传输时,
链路层在分组前加帧头,分组后加帧尾,相当于封装。
考点:考查封装的概念
答:
nh/(M+nh)
考点:考查TCP和UDP概念的区别
答:TCP 提供可靠的面向连接的服务,字节流;而UDP 提供不可靠的无连接服务,报文流。
考点:
考点:对层次通信模型的理解
答:服务是垂直的,并且是下层向上层提供。k+1层要调用第k层的服务,对k+1层有影响,对k-1层无影响。
注意:协议是对等层的
本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)