Android动画目前分为三种: 补间动画和属性动画的区别 下面就从源码分析三种动画是如何生效,还有补间动画和属性动画的区别 找一种最简单的补间动画开始来分析补间动画是怎么生效的 看看 View 是如何开始动画的 View 进行重绘,必然要重新执行 draw 方法,这里也是动画最终执行的地方 先看第一部分,如何获取动画对 View 的偏移值,设置到 transformToApply 属性上 调用 Animation.getTransformation 方法来获取 Transformation applyTransformation 方法在 Animation 中是一个空实现,具体看移动动画的实现 TranslateAnimation 这里设置结束,也就相当于 parent.getChildTransformation() 设置了 dx 和 dy 的偏移 接下来,看下第二部分:把动画对 View 的偏移值绘制到屏幕上 这也是补间动画,View 移动之后为什么不可以点击的原因。 同样找一种最简单的属性动画开始来分析属性动画是怎么生效的 首先是对 ObjectAnimator 进行动画参数的设置 需要 ObjectAnimator 的父类 ValueAnimator 进行设置记录 接下来真正开始动画 ObjectAnimator 的父类 ValueAnimator 真正开始动画 在 AnimationHandler 加入 addAnimationFrameCallback 的回调 addAnimationFrameCallback 方法只是把 callback 加入到了 mAnimationCallbacks 集合当中,我们来找下,哪里具体回调了 callback 继续往上回溯,找到调用 doAnimationFrame 的方法,是在 mFrameCallback 里面的 看来就是前面 addAnimationFrameCallback 方法里面,第一次添加 callback 的时候加上去的,具体分析下 getProvider().postFrameCallback(mFrameCallback); 方法 接下来看下 MyFrameCallbackProvider 具体是什么。 再回到 ValueAnimator.start 方法看 startAnimation 做了什么。 通过前面的 AnimationHandler.addAnimationFrameCallback 方法已经知道,Choreographer 会每 16ms 回调一次 doFrame 方法,而 doFrame 方法会调用 callback.doAnimationFrame ObjectAnimator 对 animateValue 有自己的而实现 具体到 setAnimatedValue 看下怎么调用 mJniSetter 是前面就设置好的,通过 setupSetter 提前已经设好了,而 setupSetter 的时机是在动画初始化的时候,ObjectAnimator.initAnimation 方法中调用的,详细可以自己去看 最终调用的 View 里面的 setTranslationX 方法 View 的 setTranslationX,还是调用 RenderNode 里面的 native 方法,进行硬件加速动画绘制 下面是完整的调用链 总结一下属性动画更新的原理:通过 Choreographer 会每 16ms 回调一次 doFrame 方法,在 doFrame 方法里不断地更新 View 的属性以达到动画的效果。 那么问题来了,属性动画并没有更新 View 的位置属性 left, right, top, botoom, 为什么和补间动画不一样,这个 View 还可以点击呢? 其实,这个问题也很简单,在 dispatchTouchEvent 进行触摸事件分发的时候,对 View 的位置进行了一次转换 获取当前 View 的转换矩阵 最终,还是要通过硬件加速的数据获取,setTranslationX 也最终会反应到这个 matrix 当中,有兴趣可以自己调试看下参数 同样找一种最简单的逐帧动画开始来分析逐帧动画是怎么生效的 开始逐帧动画 具体怎么设置第一帧动画 scheduleSelf 是父类 Drawable 实现的 那这个 getCallback 拿到的是哪里设置的呢?只有一个 setCallback 方法 可以找到 setCallback 是 View.setBackgroundDrawable 方法的时候调用的, 接下来看下 callback 是什么时候回调的。也是通过 mChoreographer 实例来回调,每 16ms 回调一次。 看看 callback 回调中做了什么,找到 run 方法。
从源码分析 Android 动画如何展现到屏幕上:补间动画、属性动画、帧动画
1. 补间动画
TranslateAnimation translateAnimation = new TranslateAnimation(0, 300.0f, 0, 0); translateAnimation.setDuration(2 * 1000); translateAnimation.setFillAfter(true); imageView.startAnimation(translateAnimation);
android.view.Viewpublic void startAnimation(Animation animation) { animation.setStartTime(Animation.START_ON_FIRST_FRAME); // 记录下需要的动画 setAnimation(animation); invalidateParentCaches(); // 进行重绘 invalidate(true); } public void setAnimation(Animation animation) { mCurrentAnimation = animation; if (animation != null) { // If the screen is off assume the animation start time is now instead of // the next frame we draw. Keeping the START_ON_FIRST_FRAME start time // would cause the animation to start when the screen turns back on if (mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mDisplayState == Display.STATE_OFF && animation.getStartTime() == Animation.START_ON_FIRST_FRAME) { animation.setStartTime(AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis()); } animation.reset(); } }
android.view.Viewboolean draw(Canvas canvas, ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime) { final boolean hardwareAcceleratedCanvas = canvas.isHardwareAccelerated(); /* If an attached view draws to a HW canvas, it may use its RenderNode + DisplayList. * * If a view is dettached, its DisplayList shouldn't exist. If the canvas isn't * HW accelerated, it can't handle drawing RenderNodes. */ ... // 第一部分:获取动画对 View 的偏移值,设置到 transformToApply 属性上 Transformation transformToApply = null; boolean concatMatrix = false; final boolean scalingRequired = mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mScalingRequired; final Animation a = getAnimation(); if (a != null) { more = applyLegacyAnimation(parent, drawingTime, a, scalingRequired); concatMatrix = a.willChangeTransformationMatrix(); if (concatMatrix) { mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_TRANSFORM; } transformToApply = parent.getChildTransformation(); } ... // 把动画对 View 的偏移值绘制到屏幕上 float alpha = drawingWithRenderNode ? 1 : (getAlpha() * getTransitionAlpha()); if (transformToApply != null || alpha < 1 || !hasIdentityMatrix() || (mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_ALPHA) != 0) { if (transformToApply != null || !childHasIdentityMatrix) { int transX = 0; int transY = 0; if (offsetForScroll) { transX = -sx; transY = -sy; } if (transformToApply != null) { if (concatMatrix) { if (drawingWithRenderNode) { renderNode.setAnimationMatrix(transformToApply.getMatrix()); } else { // Undo the scroll translation, apply the transformation matrix, // then redo the scroll translate to get the correct result. canvas.translate(-transX, -transY); canvas.concat(transformToApply.getMatrix()); canvas.translate(transX, transY); } parent.mGroupFlags |= ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION; } float transformAlpha = transformToApply.getAlpha(); if (transformAlpha < 1) { alpha *= transformAlpha; parent.mGroupFlags |= ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION; } } if (!childHasIdentityMatrix && !drawingWithRenderNode) { canvas.translate(-transX, -transY); canvas.concat(getMatrix()); canvas.translate(transX, transY); } } ... }
android.view.Viewprivate boolean applyLegacyAnimation(ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime, Animation a, boolean scalingRequired) { Transformation invalidationTransform; ... final Transformation t = parent.getChildTransformation(); boolean more = a.getTransformation(drawingTime, t, 1f); ... }
根据 getTransformation 的方法名就可以知道,第二个参数是用来重新设置的,所以会把动画的属性设置到 parent.getChildTransformation() 上
android.view.animation.Animationpublic boolean getTransformation(long currentTime, Transformation outTransformation, float scale) { mScaleFactor = scale; return getTransformation(currentTime, outTransformation); } public boolean getTransformation(long currentTime, Transformation outTransformation) { ... // 根据当前时间和补偿器来获取当前的 Transformation final float interpolatedTime = mInterpolator.getInterpolation(normalizedTime); applyTransformation(interpolatedTime, outTransformation); ... }
android.view.animation.TranslateAnimationprotected void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime, Transformation t) { float dx = mFromXDelta; float dy = mFromYDelta; // 根据补偿器时间来计算当前需要偏移的 dx 和 dy,并只是到 Transformation 上 if (mFromXDelta != mToXDelta) { dx = mFromXDelta + ((mToXDelta - mFromXDelta) * interpolatedTime); } if (mFromYDelta != mToYDelta) { dy = mFromYDelta + ((mToYDelta - mFromYDelta) * interpolatedTime); } t.getMatrix().setTranslate(dx, dy); }
后面 transformToApply = parent.getChildTransformation() ,transformToApply就相当于设置过偏移的 Transformation 实例了
android.view.Viewboolean draw(Canvas canvas, ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime) { final boolean hardwareAcceleratedCanvas = canvas.isHardwareAccelerated(); /* If an attached view draws to a HW canvas, it may use its RenderNode + DisplayList. * * If a view is dettached, its DisplayList shouldn't exist. If the canvas isn't * HW accelerated, it can't handle drawing RenderNodes. */ ... // 把动画对 View 的偏移值绘制到屏幕上 float alpha = drawingWithRenderNode ? 1 : (getAlpha() * getTransitionAlpha()); if (transformToApply != null || alpha < 1 || !hasIdentityMatrix() || (mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_ALPHA) != 0) { if (transformToApply != null || !childHasIdentityMatrix) { int transX = 0; int transY = 0; if (offsetForScroll) { transX = -sx; transY = -sy; } if (transformToApply != null) { if (concatMatrix) { if (drawingWithRenderNode) { renderNode.setAnimationMatrix(transformToApply.getMatrix()); } else { // Undo the scroll translation, apply the transformation matrix, // then redo the scroll translate to get the correct result. canvas.translate(-transX, -transY); // 把 transformToApply 的偏移应用到 canvas 上 canvas.concat(transformToApply.getMatrix()); canvas.translate(transX, transY); } parent.mGroupFlags |= ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION; } float transformAlpha = transformToApply.getAlpha(); if (transformAlpha < 1) { alpha *= transformAlpha; parent.mGroupFlags |= ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION; } } if (!childHasIdentityMatrix && !drawingWithRenderNode) { canvas.translate(-transX, -transY); canvas.concat(getMatrix()); canvas.translate(transX, transY); } } ... }
因为补间动画是通过 canvas 画布进行偏移绘制,而 View 的属性 left, right, top, bottom 都没改变,相当于对 View 进行触摸事件分发还在原来的地方。
所以,点击原来位置可以响应,新的位置不响应。2. 属性动画
ObjectAnimator animator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView, "translationX", 0, 300); animator.setDuration(2 * 1000); animator.start();
android.animation.ObjectAnimatorpublic static ObjectAnimator ofFloat(Object target, String propertyName, float... values) { ObjectAnimator anim = new ObjectAnimator(target, propertyName); // 设置动画参数 anim.setFloatValues(values); return anim; } public void setFloatValues(float... values) { if (mValues == null || mValues.length == 0) { // No values yet - this animator is being constructed piecemeal. Init the values with // whatever the current propertyName is if (mProperty != null) { setValues(PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat(mProperty, values)); } else { // 设置动画参数 setValues(PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat(mPropertyName, values)); } } else { super.setFloatValues(values); } }
android.animation.ValueAnimatorpublic void setValues(PropertyValuesHolder... values) { int numValues = values.length; // 记录下动画的参数,后面具体做动画时会使用到 mValues = values; mValuesMap = new HashMap<String, PropertyValuesHolder>(numValues); for (int i = 0; i < numValues; ++i) { PropertyValuesHolder valuesHolder = values[i]; mValuesMap.put(valuesHolder.getPropertyName(), valuesHolder); } // New property/values/target should cause re-initialization prior to starting mInitialized = false; }
android.animation.ObjectAnimatorpublic void start() { ... super.start(); }
android.animation.ValueAnimatorpublic void start() { start(false); } private void start(boolean playBackwards) { ... // 增加动画的回调 addAnimationCallback(0); if (mStartDelay == 0 || mSeekFraction >= 0 || mReversing) { // If there's no start delay, init the animation and notify start listeners right away // to be consistent with the previous behavior. Otherwise, postpone this until the first // frame after the start delay. // 开始动画 startAnimation(); if (mSeekFraction == -1) { // No seek, start at play time 0. Note that the reason we are not using fraction 0 // is because for animations with 0 duration, we want to be consistent with pre-N // behavior: skip to the final value immediately. // 设置第一帧动画,进行开始 setCurrentPlayTime(0); } else { setCurrentFraction(mSeekFraction); } } } // 增加动画的回调 private void addAnimationCallback(long delay) { if (!mSelfPulse) { return; } getAnimationHandler().addAnimationFrameCallback(this, delay); }
android.animation.AnimationHandlerpublic void addAnimationFrameCallback(final AnimationFrameCallback callback, long delay) { // 第一次加入 callback 回调的时候,加入 mFrameCallback 回调 if (mAnimationCallbacks.size() == 0) { getProvider().postFrameCallback(mFrameCallback); } // 只是把 callback 回调加入到 mAnimationCallbacks 的集合当中 if (!mAnimationCallbacks.contains(callback)) { mAnimationCallbacks.add(callback); } if (delay > 0) { mDelayedCallbackStartTime.put(callback, (SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delay)); } }
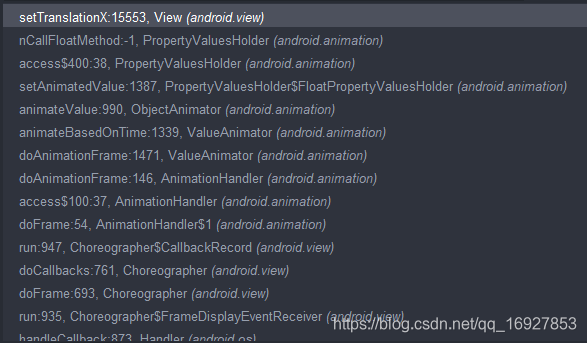
通过搜索可以快速找到在 doAnimationFrame 方法里回调了 callback 方法
android.animation.AnimationHandlerprivate void doAnimationFrame(long frameTime) { long currentTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); final int size = mAnimationCallbacks.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { final AnimationFrameCallback callback = mAnimationCallbacks.get(i); if (callback == null) { continue; } if (isCallbackDue(callback, currentTime)) { callback.doAnimationFrame(frameTime); if (mCommitCallbacks.contains(callback)) { getProvider().postCommitCallback(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { commitAnimationFrame(callback, getProvider().getFrameTime()); } }); } } } cleanUpList(); }
android.animation.AnimationHandlerprivate final Choreographer.FrameCallback mFrameCallback = new Choreographer.FrameCallback() { @Override public void doFrame(long frameTimeNanos) { doAnimationFrame(getProvider().getFrameTime()); if (mAnimationCallbacks.size() > 0) { getProvider().postFrameCallback(this); } } };
看到 getProvider 拿到的是 MyFrameCallbackProvider
android.animation.AnimationHandlerprivate AnimationFrameCallbackProvider getProvider() { if (mProvider == null) { mProvider = new MyFrameCallbackProvider(); } return mProvider; }
里面直接通过 Choreographer.getInstance() 方法拿到了当前线程的 mChoreographer对象。
getProvider().postFrameCallback(mFrameCallback) 就是调用 mChoreographer.postFrameCallback(callback)
Choreographer 会每 16ms 回调一次 doFrame 方法
android.animation.AnimationHandlerprivate class MyFrameCallbackProvider implements AnimationFrameCallbackProvider { final Choreographer mChoreographer = Choreographer.getInstance(); @Override public void postFrameCallback(Choreographer.FrameCallback callback) { mChoreographer.postFrameCallback(callback); } @Override public void postCommitCallback(Runnable runnable) { mChoreographer.postCallback(Choreographer.CALLBACK_COMMIT, runnable, null); } @Override public long getFrameTime() { return mChoreographer.getFrameTime(); } @Override public long getFrameDelay() { return Choreographer.getFrameDelay(); } @Override public void setFrameDelay(long delay) { Choreographer.setFrameDelay(delay); } }
其实就是做了一些初始化动画和通知动画开始的回调
android.animation.ValueAnimatorprivate void startAnimation() { if (Trace.isTagEnabled(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW)) { Trace.asyncTraceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, getNameForTrace(), System.identityHashCode(this)); } mAnimationEndRequested = false; initAnimation(); mRunning = true; if (mSeekFraction >= 0) { mOverallFraction = mSeekFraction; } else { mOverallFraction = 0f; } if (mListeners != null) { notifyStartListeners(); } } void initAnimation() { if (!mInitialized) { int numValues = mValues.length; for (int i = 0; i < numValues; ++i) { mValues[i].init(); } mInitialized = true; } }
看下 ValueAnimator.doAnimationFrame 做了什么public final boolean doAnimationFrame(long frameTime) { ... // 计算当前的时间 final long currentTime = Math.max(frameTime, mStartTime); boolean finished = animateBasedOnTime(currentTime); if (finished) { endAnimation(); } return finished; } boolean animateBasedOnTime(long currentTime) { boolean done = false; if (mRunning) { // 根据时间计算得到,当前的比例 float currentIterationFraction = getCurrentIterationFraction( mOverallFraction, mReversing); // 设置动画具体值,改变 View 位置关键所在 animateValue(currentIterationFraction); } return done; }
android.animation.ObjectAnimatorvoid animateValue(float fraction) { final Object target = getTarget(); if (mTarget != null && target == null) { // We lost the target reference, cancel and clean up. Note: we allow null target if the /// target has never been set. cancel(); return; } super.animateValue(fraction); int numValues = mValues.length; for (int i = 0; i < numValues; ++i) { mValues[i].setAnimatedValue(target); } }
android.animation.PropertyValuesHolder$FloatPropertyValuesHoldervoid setAnimatedValue(Object target) { ... if (mJniSetter != 0) { nCallFloatMethod(target, mJniSetter, mFloatAnimatedValue); return; } ... }
android.animation.PropertyValuesHolder$FloatPropertyValuesHolder void setupSetter(Class targetClass) { ... if (!wasInMap) { String methodName = getMethodName("set", mPropertyName); try { mJniSetter = nGetFloatMethod(targetClass, methodName); } catch (NoSuchMethodError e) { // Couldn't find it via JNI - try reflection next. Probably means the method // doesn't exist, or the type is wrong. An error will be logged later if // reflection fails as well. } if (propertyMap == null) { propertyMap = new HashMap<String, Long>(); sJNISetterPropertyMap.put(targetClass, propertyMap); } propertyMap.put(mPropertyName, mJniSetter); } ... } // 这里的 propertyName = translationX, 返回为函数名为 "setTranslationX" static String getMethodName(String prefix, String propertyName) { if (propertyName == null || propertyName.length() == 0) { // shouldn't get here return prefix; } char firstLetter = Character.toUpperCase(propertyName.charAt(0)); String theRest = propertyName.substring(1); return prefix + firstLetter + theRest; }
android.view.Viewpublic void setTranslationX(float translationX) { if (translationX != getTranslationX()) { invalidateViewProperty(true, false); mRenderNode.setTranslationX(translationX); invalidateViewProperty(false, true); invalidateParentIfNeededAndWasQuickRejected(); notifySubtreeAccessibilityStateChangedIfNeeded(); } }
android.view.RenderNodepublic boolean setTranslationX(float translationX) { return nSetTranslationX(mNativeRenderNode, translationX); }
android.view.ViewGrouppublic boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) { mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onTouchEvent(ev, 1); } ... if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, cancelChild, target.child, target.pointerIdBits)) { handled = true; } ... } // 对子 View 进行转黄 private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel, View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) { final boolean handled; ... if (child == null) { handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent); } else { final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft; final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop; transformedEvent.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY); // 判断子 View 是否需要转换 if (! child.hasIdentityMatrix()) { transformedEvent.transform(child.getInverseMatrix()); } handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent); } // Done. transformedEvent.recycle(); return handled; }
android.view.Viewpublic final Matrix getInverseMatrix() { ensureTransformationInfo(); if (mTransformationInfo.mInverseMatrix == null) { mTransformationInfo.mInverseMatrix = new Matrix(); } final Matrix matrix = mTransformationInfo.mInverseMatrix; mRenderNode.getInverseMatrix(matrix); return matrix; }
android.view.RenderNodepublic void getInverseMatrix(@NonNull Matrix outMatrix) { nGetInverseTransformMatrix(mNativeRenderNode, outMatrix.native_instance); } 3. 逐帧动画
AnimationDrawable animationDrawable=(AnimationDrawable) getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.frame_animation); view.setBackgroundDrawable(animationDrawable); animationDrawable.start()
android.graphics.drawable.AnimationDrawablepublic void start() { mAnimating = true; if (!isRunning()) { // Start from 0th frame. // 设置为第一帧 setFrame(0, false, mAnimationState.getChildCount() > 1 || !mAnimationState.mOneShot); } }
android.graphics.drawable.AnimationDrawableprivate void setFrame(int frame, boolean unschedule, boolean animate) { if (frame >= mAnimationState.getChildCount()) { return; } mAnimating = animate; mCurFrame = frame; // 设置为相应帧 Drawable selectDrawable(frame); if (unschedule || animate) { // 结束的时候停止循环更新 unscheduleSelf(this); } if (animate) { // Unscheduling may have clobbered these values; restore them mCurFrame = frame; mRunning = true; // 把自己加入循环中,不断收到消息更新动画帧 scheduleSelf(this, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + mAnimationState.mDurations[frame]); } }
android.graphics.drawable.Drawablepublic void scheduleSelf(@NonNull Runnable what, long when) { final Callback callback = getCallback(); if (callback != null) { // 在 callback 中具体加入 callback.scheduleDrawable(this, what, when); } }
android.graphics.drawable.Drawablepublic final void setCallback(@Nullable Callback cb) { mCallback = cb != null ? new WeakReference<>(cb) : null; }
android.view.Viewpublic void setBackgroundDrawable(Drawable background) { computeOpaqueFlags(); ... background.setCallback(this); }
android.view.Viewpublic void scheduleDrawable(@NonNull Drawable who, @NonNull Runnable what, long when) { if (verifyDrawable(who) && what != null) { final long delay = when - SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); if (mAttachInfo != null) { mAttachInfo.mViewRootImpl.mChoreographer.postCallbackDelayed( Choreographer.CALLBACK_ANIMATION, what, who, Choreographer.subtractFrameDelay(delay)); } else { // Postpone the runnable until we know // on which thread it needs to run. getRunQueue().postDelayed(what, delay); } } } public void run() { nextFrame(false); } private void nextFrame(boolean unschedule) { // 帧数加一 int nextFrame = mCurFrame + 1; final int numFrames = mAnimationState.getChildCount(); final boolean isLastFrame = mAnimationState.mOneShot && nextFrame >= (numFrames - 1); // Loop if necessary. One-shot animations should never hit this case. if (!mAnimationState.mOneShot && nextFrame >= numFrames) { nextFrame = 0; } // 不断循环调用 setFrame,知道结尾帧 setFrame(nextFrame, unschedule, !isLastFrame); }
本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)