在前面的篇章Android 9 Zygote进程启动源码分析指南中我们重点分析了zygote启动的流程,但是剩余了两个重点的知识点没有讲解其中之一就是Android system_server进程启动的完整流程,在本篇中我们将要揭开system_server的神秘面纱分析分析它究竟是怎么启动的。 SystemServer进程是zygote进程启动后,主动“分裂”的第一个进程。如果说zygote孵化了整个Android的Java世界,那么system_server进程就是它的左膀右臂一起掌管Android的Java世界。它负责启动大量的Android系统核心服务,其重要性不言而喻。一旦该进程崩溃,整个Android系统将重新启动。 注意:本文演示的代码是Android P高通msm8953平台源码。其中涉及的源码路径如下: 在正式开始源码前,先奉上system_server进程启动的整体流程图,这样有助于童靴们心里构建一个整体的流程图谱,这样就可以根据图谱再结合源码达到一一击破,逐个分析的功效。再说有图才有真相不是! 在前面的篇章Android 9 Zygote进程启动源码分析指南中我们知道当zygote进程进入到java世界后,在ZygoteInit.java中,将调用startSystemServer函数启动SystemServer进程,其关键代码是: 我们重点关注forkSystemServer,大伙该上厕所的先上厕所,该喝水的先喝水内容比较多额。 该代码定义在ZygoteInit.java中 从上述源码我们可以看出,该代码的逻辑划分如下: 代码定义在Zygote.java中 通过前面我们对zygote启动的流程分析我们可知Android系统的JNI函数绝大分布都是在androidRuntime.cpp中进行注册的,nativeForkSystemServer()本地方法也不例外。这里nativeForkSystemServer会调用com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp中的register_com_android_internal_os_Zygote()方法建立native方法的映射关系,所以接下来进入如下方法。 这里有一个小窍门,怎么找到Android系统中Java的本地方法对应的Jni所在文件呢,一般的规则如下: 通过前面章节我们知道nativeForkSystemServer是一个本地方法,最终通过Jni调用到了com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp中的com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkSystemServer中,代码逻辑如下所示: 通过上面的代码可以看到,当system_server创建如果夭折了的话,那么Android将不得不重启zygote进程了。但是需要注意的是,对于Android 5.0以上系统,有两个zygote进程,分别是zygote、zygote64两个进程,system_server的父进程,一般来说64位系统其父进程是zygote64进程(这个是参考gityuan的,不保证正确)。 这里提供一个小方法教大伙看系统中那些进程是由zygote64启动的那些是由zygote启动的,具体的步骤如下: 该代码依然还是定义在com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp中,冗余细节有点多,我们这里只抓主要的,细节的现行放过。 这里可以看到ForkAndSpecializeCommon函数最终调用的是fork()函数创建新的进程,而fork创建进程采用的是COW(写时拷贝技术)这是linux创建进程的标准方法,会有两次return,对于pid==0为子进程的返回,对于pid>0为父进程的返回。 在文章的开篇我们说到,zygote进程和system_server几乎是同生共死,休戚相关的,那是怎么做到的呢?这里我们看到在zygote进程fork之前,调用SetSigChldHandler函数注册了一个子进程信号监听器。由于子进程共享父进程中的堆及栈信息,因此在子进程中也会有相应的信号处理器。为了避免该信号监听器对子进程的影响,可以看到在子进程中进行了UnsetSigChldHandler的操作。zygote进程和system_server同生共死的密码就在SetSigChldHandler中了。 该代码依然还是定义在com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp中,我们看看它究竟做了些什么什么操作! 这个代码并不神秘,在前面讲解init进程源码分析中也分析过类似的。在这里注册一个信号处理器,来监听子进程的死亡。当子进程死亡后,利用SigChldHandler进行操作。需要注意的是,zygote的信号监听器,关注的是zygote所有的子进程,而不只是SystemServer进程(每次创建一个新的进程时,zygote都会注册对应的监听器)。 让我们继续分析SigChldHandler看看它做了些什么工作 看到这里大伙应该明白了,所有zygote的子进程中,zygote只关心了SystemServer的死活。当其它子进程crash时,zygote只打印了log信息(有点天要下雨娘要嫁人随他去的感觉)。看来我们的zygote是有点偏心长子啊。 对于system_server进程恢复默认信号处理,此时的我脑海中浮现了一个画面zygote进程对system_server说孩儿好好干,当爹的不会亏待你的。 到此system_server进程已完成了创建的所有工作,接下来开始了system_server进程的真正工作。在前面startSystemServer()方法中,zygote进程执行完forkSystemServer()后,新创建出来的system_server进程便进入handleSystemServerProcess()方法。 兜兜转转又回到了ZygoteInit.java中的handleSystemServerProcess方法中 从上面的代码可以看出,接下来的流程进入到ZygoteInit的zygoteInit函数。zygoteInit函数将根据classLoader和参数,完成不同进程所需要的初始化工作(SystemServer进程与zygote的其它子进程均将使用zygoteInit函数)。 在分析performSystemServerDexOpt我们先来看看Os.getenv(“SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH”)获取的环境变量是什么,关于怎么通过adb查看Android系统环境变量可以参见如下博客Android获取和设置系统环境变量指南,SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH 环境变量值如下: 了解了performSystemServerDexOpt的传入参数,我们接着继续分析下面的代码,该代码的逻辑如下: 在前面的2.5章节我们知道parsedArgs.invokeWith属性默认为null,最后调用RuntimeInit.zygoteInit来进一步启动system_server进程。在zygoteInit中执行的主要代码逻辑如下: 该代码定义在frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java中,主要是做了一些常规的初始化,从逻辑上分析主要分为如下几个方面: 这其中User-Agent是Http协议中的一部分,属于头域的组成部分,是一种向访问网站者提供你所使用的浏览器类型,操作系统,浏览器内核等信息的标识。通过这个标识,用户所访问的网站可以显示不同的排版,从而为用户提供更好的体验或者进行信息统计。 一看方法名称就知道是要调用native方法进行初始化,通过调用nativeZygoteInit主要是用来启动Binder线程池的。该方法nativeZyoteInit实现在frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp中,对应的JNI映射如下所示: 通过JNI的gMethods数组,可以看出nativeZygoteInit函数对应的是JNI文件AndroidRuntime.cpp的com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeZygoteInit函数: 这里可以看到gCurRuntime是AndroidRuntime类型的指针,可是AndroidRuntime的onZygoteInit却是一个虚函数,那么就应该在其子类中实现了。那么gCurRuntime究竟指的是什么呢? 在我们前面的篇章中介绍zygote启动过程中,在app_main.cpp的main函数中,创建出了AppRuntime对象,其逻辑如下: 而AppRuntime 的定义也在app_main.c中其如下: 接着继续来看看AppRuntime的父类AndroidRuntime的代码: 从代码可以看出,AndroidRuntime初始化时定义了gCurRuntime。gCurRuntime指向对象自身,也就是说gCurRuntime指向的是AppRuntime对象(有时候感觉继承搞起来是比较麻烦,我们驱动的同事就说看着面向对象里面那一堆堆的继承,就头疼)。 由于SystemServer进程由zygote进程fork出来,于是system server进程中也存在gCurRuntime对象,类型为AppRuntime。至此我们知道,Native函数中gCurRuntime->onZygoteInit将调用AppRuntime中的onZygoteInit。 ProcessState::self()是单例模式,主要工作是调用open()打开/dev/binder驱动设备,再利用mmap()映射内核的地址空间,将Binder驱动的fd赋值ProcessState对象中的变量mDriverFD,用于交互操作。startThreadPool()是创建一个新的binder线程,不断进行talkWithDriver(),在binder系列文章中Android Binder入门指南之Binder服务的消息循环有关于该详细的讲解,这里就不过多阐述了。这样将当前线程注册到Binder驱动程序中,这样我们创建的线程就加入了Binder线程池中,这样新创建的SyetemServer进程就支持Binder进程间通信了。 继续回到ZygoteInit.java类中的applicationInit看看它做了些什么,applicationInit定义在RuntimeInit.java中,其主要逻辑如下: 接着分析findStaticMain方法,其中传递进来的参数className是om.android.server.SystemServer ,所以其主要逻辑如下: 这里有一点需要重点注意的,在Android 8之前的版本都是通过直接在MethodAndArgsCaller抛出该异常,然后在ZygoteInit.java中的main方法中捕获,但是Android 8及以后都改变了这种策略是通过返回MethodAndArgsCaller,然后在main中直接调用,其逻辑如下所示,接着判断Runnable 是否为空,如果不为空则调用run方法 在ZygoteInit.java中的main方法中运行r.run直捣黄龙,启动SystemServer的main方法。 经过层层的拨山涉水,我们终于总算是进入到了SystemServer类的main()方法,但是这还只是分析system_server进程的开端,在后续的篇章中我们将要真正的分析system_server进程真的干了什么,为啥它能在Android的世界里面如此位高权重。
Android 9 系统启动之SystemServer大揭秘上
前言
开篇
SystemServer对Android意味着什么?这个答案是不言而喻的,它是Android Java世界的精神支柱,虽然Android的Java世界可以说由zygote孵化而来的,但是在我看来zygote也是一个甩手掌柜只管生,生完就不管了(有点像动物世界里的蜂王,当然我们男同袍不是的)。而system_server进程则是Android Java世界的核心管理者,为了Java世界的繁华提供着各种服务,事必亲力亲为(有点像动物世界的工蜂)。
正是由于zygote和system_server的关系如此密切,所以这两者之间任何一个发生异常,都会导致Android Java的崩溃(所有由Zygote孵化的Java进程都会被销毁,而SystemServer就是由Zygote孵化而来)。若Android Java真的崩溃了,那么Linux系统中的进程init会重新启动“两大支柱”以重建Android Java,也有可能陷入无限死循环启动不了这个就要根据实际情况看来了。frameworks//base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/Zygote.java frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java 一. system_server启动的整体概括
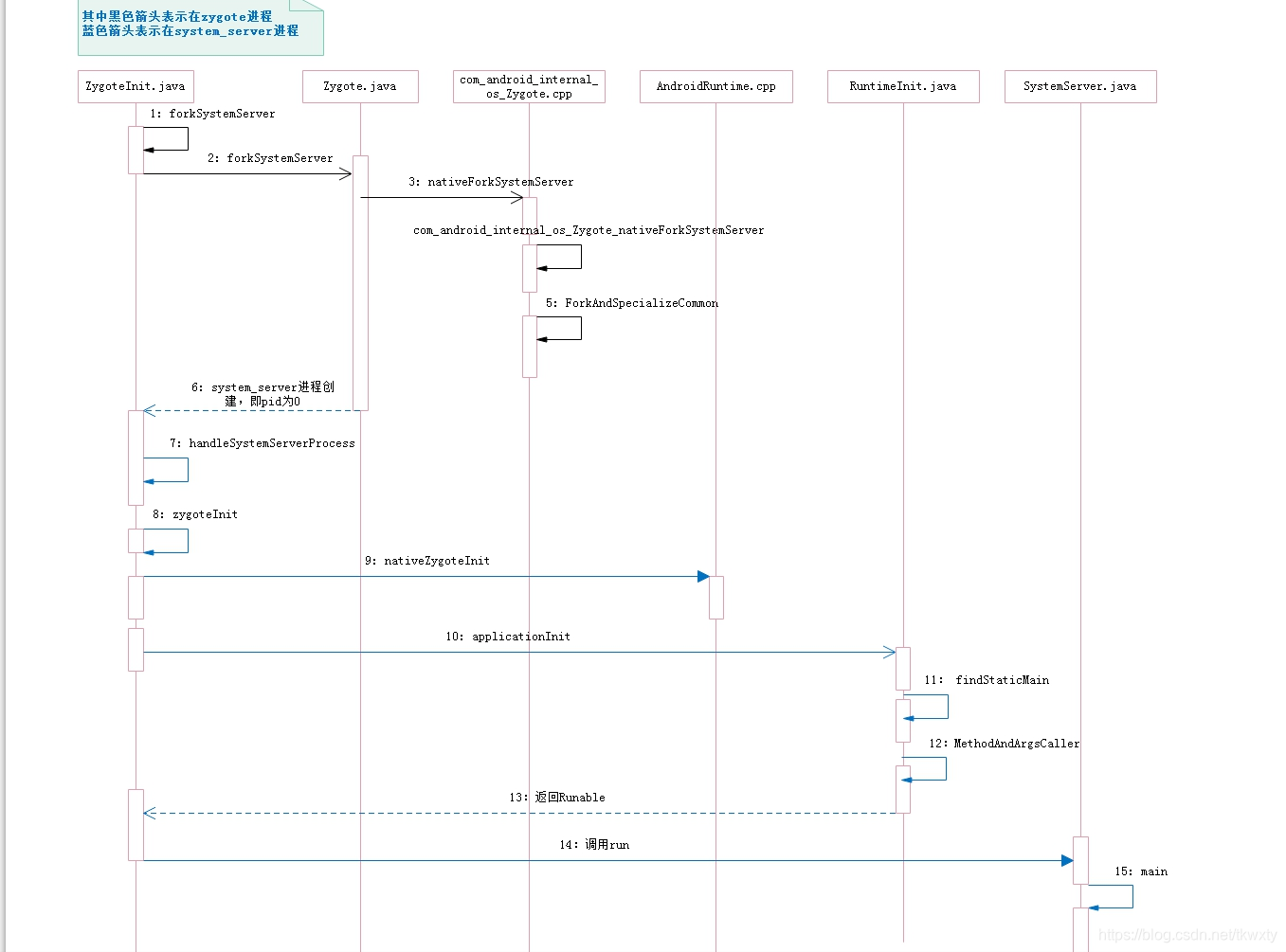
二. system_server进程启动源码分析
if (startSystemServer) { Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer); // {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the // child (system_server) process. if (r != null) { r.run(); return; } }
2.1 forkSystemServer
/** * Prepare the arguments and forks for the system server process. * * Returns an {@code Runnable} that provides an entrypoint into system_server code in the * child process, and {@code null} in the parent. */ private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName, ZygoteServer zygoteServer) { ...... //参数准备,system_server进程启动的相关参数 String args[] = { "--setuid=1000", "--setgid=1000", "--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,1024,1032,1065,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010", "--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities, "--nice-name=system_server", "--runtime-args", "--target-sdk-version=" + VMRuntime.SDK_VERSION_CUR_DEVELOPMENT, "com.android.server.SystemServer", }; ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null; int pid; try { //用于参数解析,生成目标格式 parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args); ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs); ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs); boolean profileSystemServer = SystemProperties.getBoolean( "dalvik.vm.profilesystemserver", false); if (profileSystemServer) { parsedArgs.runtimeFlags |= Zygote.PROFILE_SYSTEM_SERVER; } /* Request to fork the system server process */ //重点来了,通过forkSystemServer来fork子进程,进程是system_server pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer( parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid, parsedArgs.gids, parsedArgs.runtimeFlags, null, parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities, parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities); } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { throw new RuntimeException(ex); } /* For child process */ if (pid == 0) {//如果是子进程 if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {//如果有SecondZygote进程需要启动,等待启动完成 waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName); } zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();//关闭zygote原有socket return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);//处理system_server进程相关的事务 } return null; |
2.2 Zygote.forkSystemServer
public static int forkSystemServer(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags, int[][] rlimits, long permittedCapabilities, long effectiveCapabilities) { VM_HOOKS.preFork();//这个分支先不予分析 // Resets nice priority for zygote process. resetNicePriority(); int pid = nativeForkSystemServer( uid, gid, gids, runtimeFlags, rlimits, permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities); // Enable tracing as soon as we enter the system_server. if (pid == 0) { Trace.setTracingEnabled(true, runtimeFlags); } VM_HOOKS.postForkCommon();//先不予分析 return pid; }
1. 将Java类所在的包名中的.转换成_,譬如我们这里的Zygote所在包名为com.android.internal.os,转换后即为com_android_internal_os
2. 将上述转换后的字符串+”_”+Java类名.cpp,就是我们要找的Jni文件了,譬如我们这里的com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
2.3 nativeForkSystemServer
static jint com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkSystemServer( JNIEnv* env, jclass, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray gids, jint runtime_flags, jobjectArray rlimits, jlong permittedCapabilities, jlong effectiveCapabilities) { //划重点,fork子进程 pid_t pid = ForkAndSpecializeCommon(env, uid, gid, gids, runtime_flags, rlimits, permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities, MOUNT_EXTERNAL_DEFAULT, NULL, NULL, true, NULL, NULL, false, NULL, NULL); if (pid > 0) { // The zygote process checks whether the child process has died or not. ALOGI("System server process %d has been created", pid); //pid大于0,在父进程中即在zygote进程中 //// 将子进程SystemServer的pid存在zygote进程的全局变量中 gSystemServerPid = pid; // There is a slight window that the system server process has crashed // but it went unnoticed because we haven't published its pid yet. So // we recheck here just to make sure that all is well. int status; if (waitpid(pid, &status, WNOHANG) == pid) { //如果system_server创建即夭折了,那么就重启zygote进程只得重新开始孵化了 ALOGE("System server process %d has died. Restarting Zygote!", pid); RuntimeAbort(env, __LINE__, "System server process has died. Restarting Zygote!"); } bool low_ram_device = GetBoolProperty("ro.config.low_ram", false); bool per_app_memcg = GetBoolProperty("ro.config.per_app_memcg", low_ram_device); if (per_app_memcg) { // Assign system_server to the correct memory cgroup. // Not all devices mount /dev/memcg so check for the file first // to avoid unnecessarily printing errors and denials in the logs. if (!access("/dev/memcg/system/tasks", F_OK) && !WriteStringToFile(StringPrintf("%d", pid), "/dev/memcg/system/tasks")) { ALOGE("couldn't write %d to /dev/memcg/system/tasks", pid); } } } return pid; }
msm8953_64:/ # ps | grep zygote root 756 1 2172472 83332 poll_sched 0000000000 S zygote64 root 757 1 1599292 71024 poll_sched 0000000000 S zygote
msm8953_64:/ # cd /proc/756 msm8953_64:/proc/756 # ls -ali | grep exe 407 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 1970-01-01 08:00 exe -> /system/bin/app_process64 msm8953_64:/proc/756 # cd /proc/757 msm8953_64:/proc/757 # ls -ali | grep exe 469 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 1970-01-01 08:00 exe -> /system/bin/app_process32
msm8953_64:/ # ps | grep 757 root 757 1 1599292 71024 poll_sched 00f39f06d4 S zygote mediacodec 776 1 37576 7844 binder_thr 00ef66362c S media.codec u0_a31 2300 757 1019548 44536 SyS_epoll_ 00f39f04e8 S com.pax.pinyinime system 2757 756 1588652 45852 SyS_epoll_ 7f7df5e8f0 S org.simalliance.openmobileapi.service msm8953_64:/ # ps | grep 756 root 756 1 2172472 83332 poll_sched 7f7df5ea10 S zygote64 radio 790 1 93376 15756 hrtimer_na 7f961e9328 S /system/bin/rild system 1438 756 2384124 134304 SyS_epoll_ 7f7df5e8f0 S system_server u0_a12 1771 756 1655104 133292 SyS_epoll_ 7f7df5e8f0 S com.android.systemui system 2026 756 1639448 65892 SyS_epoll_ 7f7df5e8f0 S com.android.settings radio 2039 756 1639620 73844 SyS_epoll_ 7f7df5e8f0 S com.android.phone
2.4 ForkAndSpecializeCommon
// Utility routine to fork zygote and specialize the child process. static pid_t ForkAndSpecializeCommon(JNIEnv* env, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray javaGids, jint runtime_flags, jobjectArray javaRlimits, jlong permittedCapabilities, jlong effectiveCapabilities, jint mount_external, jstring java_se_info, jstring java_se_name, bool is_system_server, jintArray fdsToClose, jintArray fdsToIgnore, bool is_child_zygote, jstring instructionSet, jstring dataDir) { SetSignalHandlers();//注册信号监听器 pid_t pid = fork();//这个是重点,system_server进程是在这里fork出来的 if (pid == 0) {//这里是system_server进程 ...... // Clean up any descriptors which must be closed immediately if (!DetachDescriptors(env, fdsToClose, &error_msg)) {//关闭并清除文件描述符 fail_fn(error_msg); } ...... if (!is_system_server && getuid() == 0) {//对于非system_server子进程,则创建进程组 int rc = createProcessGroup(uid, getpid()); if (rc != 0) { if (rc == -EROFS) { ALOGW("createProcessGroup failed, kernel missing CONFIG_CGROUP_CPUACCT?"); } else { ALOGE("createProcessGroup(%d, %d) failed: %s", uid, pid, strerror(-rc)); } } } if (!SetGids(env, javaGids, &error_msg)) {//设置group,这个是在zygoteInit中传递过来的 fail_fn(error_msg); } if (!SetRLimits(env, javaRlimits, &error_msg)) {//设置资源limits fail_fn(error_msg); } if (!SetCapabilities(permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities, permittedCapabilities, &error_msg)) { fail_fn(error_msg); } if (!SetSchedulerPolicy(&error_msg)) {//设置调度策略 fail_fn(error_msg); } //selinxu安全上下文检查 rc = selinux_android_setcontext(uid, is_system_server, se_info_c_str, se_name_c_str); if (rc == -1) { fail_fn(CREATE_ERROR("selinux_android_setcontext(%d, %d, "%s", "%s") failed", uid, is_system_server, se_info_c_str, se_name_c_str)); } // Make it easier to debug audit logs by setting the main thread's name to the // nice name rather than "app_process". if (se_name_c_str == NULL && is_system_server) { se_name_c_str = "system_server"; } if (se_name_c_str != NULL) { SetThreadName(se_name_c_str);//设置线程名,设置线程名,设置线程名为system_server } // Unset the SIGCHLD handler, but keep ignoring SIGHUP (rationale in SetSignalHandlers). UnsetChldSignalHandler();//取消信号监听器 //这里调用的是zygote.callPostForkChildHooks() env->CallStaticVoidMethod(gZygoteClass, gCallPostForkChildHooks, runtime_flags, is_system_server, is_child_zygote, instructionSet); } else if (pid > 0) {//zygote进程 ...... } return pid; } 2.4.1 SetSignalHandlers
static void SetSignalHandlers() { struct sigaction sig_chld = {}; sig_chld.sa_handler = SigChldHandler; if (sigaction(SIGCHLD, &sig_chld, NULL) < 0) { ALOGW("Error setting SIGCHLD handler: %s", strerror(errno)); } struct sigaction sig_hup = {}; sig_hup.sa_handler = SIG_IGN; // 该信号监听器关注子进程结束,对应的处理函数为SigChldHandler if (sigaction(SIGHUP, &sig_hup, NULL) < 0) { ALOGW("Error setting SIGHUP handler: %s", strerror(errno)); } } 2.4.2 SigChldHandler
// This signal handler is for zygote mode, since the zygote must reap its children static void SigChldHandler(int /*signal_number*/) { pid_t pid; int status; // It's necessary to save and restore the errno during this function. // Since errno is stored per thread, changing it here modifies the errno // on the thread on which this signal handler executes. If a signal occurs // between a call and an errno check, it's possible to get the errno set // here. // See b/23572286 for extra information. int saved_errno = errno; while ((pid = waitpid(-1, &status, WNOHANG)) > 0) { // Log process-death status that we care about. In general it is // not safe to call LOG(...) from a signal handler because of // possible reentrancy. However, we know a priori that the // current implementation of LOG() is safe to call from a SIGCHLD // handler in the zygote process. If the LOG() implementation // changes its locking strategy or its use of syscalls within the // lazy-init critical section, its use here may become unsafe. // 通过status判断子进程结束的原因,并打印相应的log if (WIFEXITED(status)) { ALOGI("Process %d exited cleanly (%d)", pid, WEXITSTATUS(status)); } else if (WIFSIGNALED(status)) { ALOGI("Process %d exited due to signal (%d)", pid, WTERMSIG(status)); if (WCOREDUMP(status)) { ALOGI("Process %d dumped core.", pid); } } // If the just-crashed process is the system_server, bring down zygote // so that it is restarted by init and system server will be restarted // from there. if (pid == gSystemServerPid) {//而对于system_sever进程就特别处理了,看来是偏心长子啊 ALOGE("Exit zygote because system server (%d) has terminated", pid); kill(getpid(), SIGKILL); } } // Note that we shouldn't consider ECHILD an error because // the secondary zygote might have no children left to wait for. if (pid < 0 && errno != ECHILD) { ALOGW("Zygote SIGCHLD error in waitpid: %s", strerror(errno)); } errno = saved_errno; } 2.4.3 UnsetChldSignalHandler
// Sets the SIGCHLD handler back to default behavior in zygote children. static void UnsetChldSignalHandler() { struct sigaction sa; memset(&sa, 0, sizeof(sa)); sa.sa_handler = SIG_DFL; if (sigaction(SIGCHLD, &sa, NULL) < 0) { ALOGW("Error unsetting SIGCHLD handler: %s", strerror(errno)); } }
2.5 handleSystemServerProcess
if (pid == 0) { if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) { waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName); } zygoteServer.closeServerSocket(); // 关闭从zygote进程那里继承下来server socket return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs); } private static Runnable handleSystemServerProcess(ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs) { // set umask to 0077 so new files and directories will default to owner-only permissions. Os.umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO); if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) { Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);//我们通过ps查看到的system_server进程名就是在这里设置的 } final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH"); //加载SystemServer对应的文件并进行优化 if (systemServerClasspath != null) { performSystemServerDexOpt(systemServerClasspath);//这个会在2.6章节中介绍 // Capturing profiles is only supported for debug or eng builds since selinux normally // prevents it. boolean profileSystemServer = SystemProperties.getBoolean( "dalvik.vm.profilesystemserver", false); if (profileSystemServer && (Build.IS_USERDEBUG || Build.IS_ENG)) { try { prepareSystemServerProfile(systemServerClasspath); } catch (Exception e) { Log.wtf(TAG, "Failed to set up system server profile", e); } } } if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {//不会进入这个分支,所以忽略 ...... }else { ClassLoader cl = null; if (systemServerClasspath != null) { // 利用systemServerClass对应的路径构建对应的ClassLoader cl = createPathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion); Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl); } /* * Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer. */ // 将剩余参数及classLoader递交给ZygoteInit的zygoteInit函数 return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl); } /* should never reach here */ }
2.6 performSystemServerDexOpt
130|msm8953_64:/ # echo $SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH /system/framework/services.jar:/system/framework/ethernet-service.jar:/system/framework/wifi-service.jar msm8953_64:/ #
private static void performSystemServerDexOpt(String classPath) { final String[] classPathElements = classPath.split(":");//分割字符串 final IInstalld installd = IInstalld.Stub .asInterface(ServiceManager.getService("installd"));//建立和install进程通信的socket通道 final String instructionSet = VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmInstructionSet(); String classPathForElement = ""; for (String classPathElement : classPathElements) { // System server is fully AOTed and never profiled // for profile guided compilation. String systemServerFilter = SystemProperties.get( "dalvik.vm.systemservercompilerfilter", "speed"); int dexoptNeeded; try { dexoptNeeded = DexFile.getDexOptNeeded( classPathElement, instructionSet, systemServerFilter, null /* classLoaderContext */, false /* newProfile */, false /* downgrade */);//判断是否需要优化 } catch (FileNotFoundException ignored) { // Do not add to the classpath. Log.w(TAG, "Missing classpath element for system server: " + classPathElement); continue; } catch (IOException e) { // Not fully clear what to do here as we don't know the cause of the // IO exception. Add to the classpath to be conservative, but don't // attempt to compile it. Log.w(TAG, "Error checking classpath element for system server: " + classPathElement, e); dexoptNeeded = DexFile.NO_DEXOPT_NEEDED; } if (dexoptNeeded != DexFile.NO_DEXOPT_NEEDED) {//如果需要优化 final String packageName = "*"; final String outputPath = null; final int dexFlags = 0; final String compilerFilter = systemServerFilter; final String uuid = StorageManager.UUID_PRIVATE_INTERNAL; final String seInfo = null; final String classLoaderContext = getSystemServerClassLoaderContext(classPathForElement); final int targetSdkVersion = 0; // SystemServer targets the system's SDK version try { //以system权限执行dexopt优化工作 installd.dexopt(classPathElement, Process.SYSTEM_UID, packageName, instructionSet, dexoptNeeded, outputPath, dexFlags, compilerFilter, uuid, classLoaderContext, seInfo, false /* downgrade */, targetSdkVersion, /*profileName*/ null, /*dexMetadataPath*/ null, "server-dexopt"); } catch (RemoteException | ServiceSpecificException e) { // Ignore (but log), we need this on the classpath for fallback mode. Log.w(TAG, "Failed compiling classpath element for system server: " + classPathElement, e); } } classPathForElement = encodeSystemServerClassPath( classPathForElement, classPathElement); } }
2.7 zygoteInit
public static final Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) { if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) { Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote"); } Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit"); RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();//重定向Log输出 RuntimeInit.commonInit();//通用的初始化,详见章节2.8 ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();//启动Binder线程池,详见章节2.9 return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);//system_server应用初始化,详见章节2.10 }
2.8 commonInit
protected static final void commonInit() { if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Entered RuntimeInit!"); /* * set handlers; these apply to all threads in the VM. Apps can replace * the default handler, but not the pre handler. */ //对于从事应用开发的童靴来说这个是再熟悉不过的了,设置未捕获异常的处理方法 LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler(); Thread.setUncaughtExceptionPreHandler(loggingHandler); Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(new KillApplicationHandler(loggingHandler)); /* * Install a TimezoneGetter subclass for ZoneInfo.db */ /*设置时区,中国时区的为Asia/Shanghai,为啥不是北京呢 *msm8953_64:/ # getprop persist.sys.timezone *Asia/Shanghai */ TimezoneGetter.setInstance(new TimezoneGetter() { @Override public String getId() { return SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.timezone"); } }); TimeZone.setDefault(null); /* * Sets handler for java.util.logging to use Android log facilities. * The odd "new instance-and-then-throw-away" is a mirror of how * the "java.util.logging.config.class" system property works. We * can't use the system property here since the logger has almost * certainly already been initialized. */ LogManager.getLogManager().reset();//重置log配置 new AndroidConfig(); /* * Sets the default HTTP User-Agent used by HttpURLConnection. */ // 设置默认的HTTP User-agent格式,用于 HttpURLConnection。 String userAgent = getDefaultUserAgent(); System.setProperty("http.agent", userAgent); /* * Wire socket tagging to traffic stats. */ //标记socket的tag,主要用于流量统计 NetworkManagementSocketTagger.install(); /* * If we're running in an emulator launched with "-trace", put the * VM into emulator trace profiling mode so that the user can hit * F9/F10 at any time to capture traces. This has performance * consequences, so it's not something you want to do always. */ String trace = SystemProperties.get("ro.kernel.android.tracing"); if (trace.equals("1")) { Slog.i(TAG, "NOTE: emulator trace profiling enabled"); Debug.enableEmulatorTraceOutput(); } initialized = true; }
2.9 nativeZygoteInit
int register_com_android_internal_os_ZygoteInit_nativeZygoteInit(JNIEnv* env) { const JNINativeMethod methods[] = { { "nativeZygoteInit", "()V", (void*) com_android_internal_os_ZygoteInit_nativeZygoteInit }, }; return jniRegisterNativeMethods(env, "com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit", methods, NELEM(methods)); } static AndroidRuntime* gCurRuntime = NULL; AndroidRuntime::AndroidRuntime(char* argBlockStart, const size_t argBlockLength) : mExitWithoutCleanup(false), mArgBlockStart(argBlockStart), mArgBlockLength(argBlockLength) { SkGraphics::Init(); // Pre-allocate enough space to hold a fair number of options. mOptions.setCapacity(20); assert(gCurRuntime == NULL); // one per process gCurRuntime = this; } static void com_android_internal_os_ZygoteInit_nativeZygoteInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz) { //此处的gCurRuntime为AppRuntime,是在AndroidRuntime.cpp中定义的,这个会详细分析的 gCurRuntime->onZygoteInit(); } int main(int argc, char* const argv[]) { ...... AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv)); ...... } class AppRuntime : public AndroidRuntime { public: AppRuntime(char* argBlockStart, const size_t argBlockLength) : AndroidRuntime(argBlockStart, argBlockLength) , mClass(NULL) { } ...... } AndroidRuntime::AndroidRuntime(char* argBlockStart, const size_t argBlockLength) : mExitWithoutCleanup(false), mArgBlockStart(argBlockStart), mArgBlockLength(argBlockLength) { SkGraphics::Init(); // Pre-allocate enough space to hold a fair number of options. mOptions.setCapacity(20); assert(gCurRuntime == NULL); // one per process gCurRuntime = this; } virtual void onZygoteInit() { sp<ProcessState> proc = ProcessState::self(); ALOGV("App process: starting thread pool.n"); proc->startThreadPool();//开启binder线程,是不是有中似曾相识的熟悉感觉 }
2.10 applicationInit
protected static Runnable applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) { // If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process // immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to // shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the // Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause // leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits. //大概意思就是为true时,应用程序退出不会调用System.exit(),从而使一些关联hook可以顺利关闭 nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true); // We want to be fairly aggressive about heap utilization, to avoid // holding on to a lot of memory that isn't needed. //设置虚拟机的内存利用率参数值为0.75 VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f); VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion); final Arguments args = new Arguments(argv);//解析参数格式为Arguments // The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit). Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER); // Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main //调用findStaticMain做进一步操作,具体查看2.11章节 return findStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader); }
2.11 findStaticMain
protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) { Class<?> cl; try { // className为进行初始化工作的进程类名 //在forkSystemServer()方法中通过硬编码初始化参数,可知该参数为com.android.server.SystemServer cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new RuntimeException( "Missing class when invoking static main " + className, ex); } Method m; try { //获取main方法 m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class }); } catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) { throw new RuntimeException( "Missing static main on " + className, ex); } catch (SecurityException ex) { throw new RuntimeException( "Problem getting static main on " + className, ex); } //判断你修饰符 int modifiers = m.getModifiers(); if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) { throw new RuntimeException( "Main method is not public and static on " + className); } /* * This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds * by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement * clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting * up the process. */ return new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv); } if (startSystemServer) { Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer); // {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the // child (system_server) process. if (r != null) { r.run(); return; } }
2.11 MethodAndArgsCaller
static class MethodAndArgsCaller implements Runnable { /** method to call */ private final Method mMethod; /** argument array */ private final String[] mArgs; public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) { mMethod = method; mArgs = args; } public void run() { try { //根据传递过来的参数,可知此处通过反射机制调用的是SystemServer.main()方法 mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs }); } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) { throw new RuntimeException(ex); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { Throwable cause = ex.getCause(); if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) cause; } else if (cause instanceof Error) { throw (Error) cause; } throw new RuntimeException(ex); } } } 结语
本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)