LSTM (Long Short Term Memory, 长短期神经网络)是一种特殊的循环神经网络(RNN, Recurrent neural networks)。 当你读这篇文章的时候,你可以根据你对前面所读单词的理解来理解上下文。 传统神经网络的一个主要不足在于不能够真正地像人类大脑的神经元一样工作运行,往往只能够利用短期记忆或者信息。 考虑下面两个句子。 “Hyderabad” 单词指明其语言应该是“Telugu”。但是“Hyderabad”出现在句首。 本文将通过 LSTM 网络开发一个故事生成器模型。主要使用自然语言处理(NLP)进行数据预处理,使用双向LSTM进行模型构建。 创建一个包含有各种题材类型的短篇小说文本库,保存为“stories.txt”。 Frozen grass crunched beneath the steps of a shambling man. His shoes were crusted and worn, and dirty toes protruded from holes in the sides. His quivering eye scanned the surroundings: a freshly paved path through the grass, which led to a double swingset, and a picnic table off to the side with a group of parents lounging in bundles, huddled to keep warm. Squeaky clean-and-combed children giggled and bounced as they weaved through the pathways with their hot breaths escaping into the air like smoke. 接下来,我们导入必要的库并且查看数据集。 首先,我们将数据全部转换为小写,并将其按行拆分,以获得一个python语句列表。 然后我们将单词进行编码并转化为向量。为每一个单词生成索引属性,该属性返回一个包含键值对的字典,其中键是单词,值是该单词的记号。 下一步将把句子转换成基于这些标记索引的值列表。这将把一行文本(如“frozen grass crunched beneath the steps”)转换成表示单词对应的标记列表。 然后我们将遍历标记列表,并且使每个句子的长度一致,否则,用它们训练神经网络可能会很困难。主要在于遍历所有序列并找到最长的一个。一旦我们有了最长的序列长度,接下来要做的是填充所有序列,使它们的长度相同。 同时,我们需要将划分输入数据(特征)以及输出数据(标签)。其中,输入数据就是除最后一个字符外的所有数据,而输出数据则是最后一个字符。 现在,我们将对标签进行 One-hot 编码,因为这实际上是一个分类问题,在给定一个单词序列的情况下,我们可以从语料库中对下一个单词进行分类预测。 有了训练数据集后,我们就可以搭建需要的模型了: 其中,第一层是 embedding 层。第一个参数反映模型处理的单词数量,这里我们希望能够处理所有单词,所以赋值 对于训练后的效果,我们主要查看准确度和损失大小。 通过以下代码可以对训练完成的模型进行保存,以方便进一步的部署。 接下来,将应用训练好的模型进行单词预测以及生成故事。 生成故事如下: As i walked, my heart sank until he was alarmed by the voice of the hunter 所有文本库:https://gist.github.com/jayashree8/08448d1b6610e444dc7a033ef4a5aae7#file-stories-txt
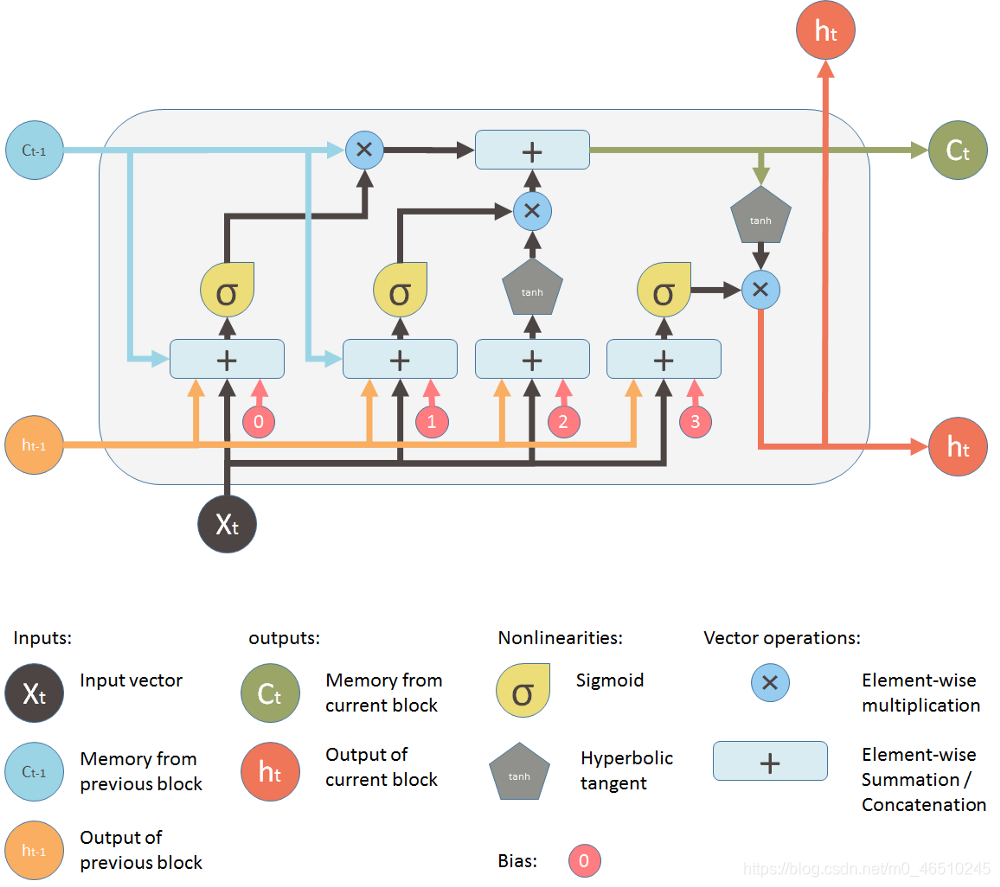
什么是 LSTM 网络?
LSTM 能够通过更新单元状态来学习参数间的长期依赖关系,目前在机器翻译、语言识别等领域有着广泛应用。LSTM 的使用背景
你不会从一开始或者从中间部分阅读就能够直接理解文本意义,而是随着你阅读的深入,你的大脑才最终形成上下文联系,能够理解文本意义。
一旦数据序列较长,就难以将早期阶段信息传递至后面阶段
如果我们要预测第一句中“<…>”的内容,那么最好的预测答案是“Telugu”。因为根据上下文,该句谈论的是 Hyderabad 的母语。
这样的预测对于人类来说是很基础的,但是对于人工神经网络而言则非常困难。
所以神经网络要准确进行预测,就必须记忆单词的所以序列。
而这正是 LSTM 可以做到的。编程实现 LSTM
Step 1:数据集准备
文本库中的一个片段如下:Step2:导入数据分析库并进行分析
使用的是运行在 TensorFlow 2.0 的 Keras 框架。from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences from tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding, LSTM, Dense, Dropout, Bidirectional from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam from tensorflow.keras import regularizers import tensorflow.keras.utils as ku import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import pickle data=open('stories.txt',encoding="utf8").read() Step3:使用 NLP 库预处理数据
转换成小写的原因是,同一单词不同大小写,其意义是一样的。例如,“Doctor”和“doctor”都是医生,但模型会对其进行不同的处理。# Converting the text to lowercase and splitting it corpus = data.lower().split("n") # Tokenization tokenizer = Tokenizer() tokenizer.fit_on_texts(corpus) total_words = len(tokenizer.word_index) + 1 print(total_words) 

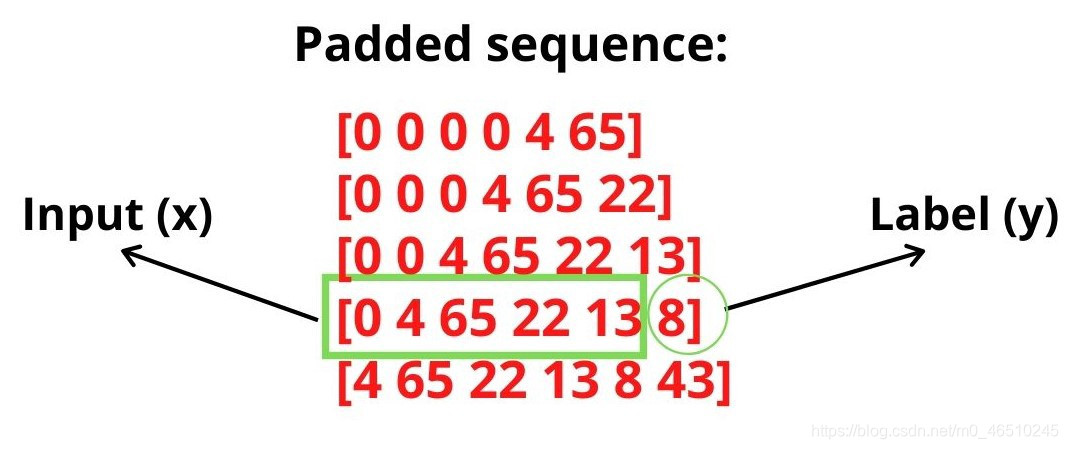
# create input sequences using list of tokens input_sequences = [] for line in corpus: token_list = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences([line])[0] for i in range(1, len(token_list)): n_gram_sequence = token_list[:i+1] input_sequences.append(n_gram_sequence) # pad sequences max_sequence_len = max([len(x) for x in input_sequences]) print(max_sequence_len) input_sequences = np.array(pad_sequences(input_sequences, maxlen=max_sequence_len, padding='pre')) # create predictors and label predictors, label = input_sequences[:,:-1],input_sequences[:,-1] label = ku.to_categorical(label, num_classes=total_words) Step 4:搭建模型
model = Sequential() model.add(Embedding(total_words, 300, input_length=max_sequence_len-1)) model.add(Bidirectional(LSTM(200, return_sequences = True))) model.add(Dropout(0.2)) model.add(LSTM(100)) model.add(Dense(total_words/2, activation='relu', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.001))) model.add(Dense(total_words, activation='softmax')) model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy']) print(model.summary()) history = model.fit(predictors, label, epochs=200, verbose=0) total_words;第二个参数反映用于绘制单词向量的维数,可以随意调整,会获得不同的预测结果;第三个参数反映输入的序列长度,因为输入序列是原始序列中除最后一个字符外的所有数据,所以这里需要减去一。
随后是 bidirectional LSTM 层以及 Dense 层。
对于损失函数,我们设置为分类交叉熵;优化函数,我们选择 adam 算法。Step 5:结果分析
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt acc = history.history['accuracy'] loss = history.history['loss'] epochs = range(len(acc)) plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'b', label='Training accuracy') plt.title('Training accuracy') plt.figure() plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'b', label='Training Loss') plt.title('Training loss') plt.legend() plt.show() 
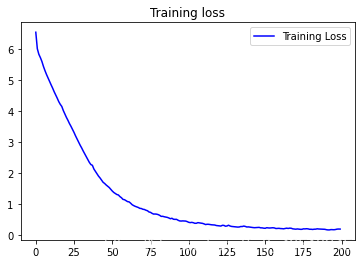
从曲线图可以看出,训练准确率不断提高,而损失则不断衰减。说明模型达到较好的性能。Step 6:保存模型
# serialize model to JSON model_json=model.to_json() with open("model.json","w") as json_file: json_file.write(model_json) # serialize weights to HDF5 model.save_weights("model.h5") print("Saved model to disk") Step 7:进行预测
首先,用户输入初始语句,然后将该语句进行预处理,输入到 LSTM 模型中,得到对应的一个预测单词。重复这一过程,便能够生成对应的故事了。具体代码如下:seed_text = "As i walked, my heart sank" next_words = 100 for _ in range(next_words): token_list = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences([seed_text])[0] token_list = pad_sequences([token_list], maxlen=max_sequence_len-1, padding='pre') predicted = model.predict_classes(token_list, verbose=0) output_word = "" for word, index in tokenizer.word_index.items(): if index == predicted: output_word = word break seed_text += " " + output_word print(seed_text)
and realised what could have happened with him he flew away the boy crunched
before it disguised herself as another effort to pull out the bush which he did
the next was a small tree which the child had to struggle a lot to pull out
finally the old man showed him a bigger tree and asked the child to pull it
out the boy did so with ease and they walked on the morning she was asked
how she had slept as a while they came back with me
本文源代码:https://github.com/jayashree8/Story_Generator/blob/master/Story_Generator.ipynb
作者:Jayashree domala
deephub翻译组:Oliver Lee
本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)